| [1] |
WONG VW, EKSTEDT M, WONG GL, et al. Changing epidemiology, global trends and implications for outcomes of NAFLD[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 3): 842- 852. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.04.036. |
| [2] |
YUAN YF, CAO Q, JIANG YY. Association of dietary behavior with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 2): 401- 407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.02.024. |
| [3] |
ZHOU JH, ZHOU F, WANG WX, et al. Epidemiological features of NAFLD from 1999 to 2018 in China[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71( 5): 1851- 1864. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31150. |
| [4] |
MAN S, DENG YH, MA Y, et al. Prevalence of liver steatosis and fibrosis in the general population and various high-risk populations: A nationwide study with 5.7 million adults in China[J]. Gastroenterology, 2023, 165( 4): 1025- 1040. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.053. |
| [5] |
RUPASINGHE K, HIND J, HEGARTY R. Updates in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease(MAFLD) in children[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2023, 77( 5): 583- 591. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0-000000000003919. |
| [6] |
LIU M, CHEN WJ, ZHOU ZZ, et al. Histopathological characteristics of the liver in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 5): 1144- 1149. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.05.021. |
| [7] |
ZHONG HX, DONG JY, ZHU LY, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis and models[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2024, 16( 2): 387- 399. DOI: 10.62347/KMSA5983. |
| [8] |
ZHAO SN, GUO Y, YIN XZ. Lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis and association with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Biosci(Landmark Ed), 2023, 28( 12): 332. DOI: 10.31083/j.fbl2812332. |
| [9] |
TIAN XB, WANG Y, LU Y, et al. Conditional depletion of macrophages ameliorates cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis via lncRNA-H19[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12( 7): 646. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03931-1. |
| [10] |
WEN YK, LAMBRECHT J, JU C, et al. Hepatic macrophages in liver homeostasis and diseases-diversity, plasticity and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18( 1): 45- 56. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-00558-8. |
| [11] |
HAN JQ, ZHANG X, LAU JK, et al. Bone marrow-derived macrophage contributes to fibrosing steatohepatitis through activating hepatic stellate cells[J]. J Pathol, 2019, 248( 4): 488- 500. DOI: 10.1002/path.5275. |
| [12] |
MAO TY, YANG R, LUO Y, et al. Crucial role of T cells in NAFLD-related disease: A review and prospect[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2022, 13: 1051076. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1051076. |
| [13] |
PAN ZY, CHAN WK, ESLAM M. The role of B cells in metabolic(dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2021, 10( 6): 875- 877. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn-21-404. |
| [14] |
CHEN SW, GUO HT, XIE MJ, et al. Neutrophil: An emerging player in the occurrence and progression of metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 97: 107609. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107609. |
| [15] |
XU M, XU H, LING YW, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps-triggered hepatocellular senescence exacerbates lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Adv Res, 2025. DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2025.03.015.[ Epub ahead of print] |
| [16] |
ZHANG KL, JAGANNATH C. Crosstalk between metabolism and epigenetics during macrophage polarization[J]. Epigenetics Chromatin, 2025, 18( 1): 16. DOI: 10.1186/s13072-025-00575-9. |
| [17] |
KAZANKOV K, JØRGENSEN SMD, THOMSEN KL, et al. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16( 3): 145- 159. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0082-x. |
| [18] |
ZHANG WH, LANG R. Macrophage metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1257596. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1257596. |
| [19] |
BARREBY E, CHEN P, AOUADI M. Macrophage functional diversity in NAFLD: More than inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2022, 18( 8): 461- 472. DOI: 10.1038/s41574-022-00675-6. |
| [20] |
VONDERLIN J, CHAVAKIS T, SIEWEKE M, et al. The multifaceted roles of macrophages in NAFLD pathogenesis[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 15( 6): 1311- 1324. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.03.002. |
| [21] |
LIU YC, ZOU XB, CHAI YF, et al. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2014, 10( 5): 520- 529. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.8879. |
| [22] |
WAN JH, BENKDANE M, TEIXEIRA-CLERC F, et al. M2 Kupffer cells promote M1 Kupffer cell apoptosis: A protective mechanism against alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59( 1): 130- 142. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26607. |
| [23] |
PANT R, KABEER SW, SHARMA S, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of DNMT1 restores macrophage autophagy and M2 polarization in Western diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Biol Chem, 2023, 299( 6): 104779. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104779. |
| [24] |
VIOLA A, MUNARI F, SÁNCHEZ-RODRÍGUEZ R, et al. The metabolic signature of macrophage responses[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1462. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01462. |
| [25] |
ANAVI S, MADAR Z, TIROSH O. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, to struggle with the strangle: Oxygen availability in fatty livers[J]. Redox Biol, 2017, 13: 386- 392. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.06.008. |
| [26] |
LIN XF, CUI XN, YANG J, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors ameliorate NAFLD in mice via downregulating PFKFB3, suppressing glycolysis and modulating macrophage polarization[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2024, 45( 12): 2579- 2597. DOI: 10.1038/s41401-024-01389-3. |
| [27] |
LIN H, ZHU LX, BAKER SS, et al. Secreted phosphoglucose isomerase is a novel biomarker of nonalcoholic fatty liver in mice and humans[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 529( 4): 1101- 1105. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.126. |
| [28] |
XU F, GUO MM, HUANG W, et al. Annexin A5 regulates hepatic macrophage polarization via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates NASH[J]. Redox Biol, 2020, 36: 101634. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101634. |
| [29] |
YU Q, WANG YF, DONG L, et al. Regulations of glycolytic activities on macrophages functions in tumor and infectious inflammation[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2020, 10: 287. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00287. |
| [30] |
WANG FL, ZHANG S, VUCKOVIC I, et al. Glycolytic stimulation is not a requirement for M2 macrophage differentiation[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 28( 3): 463- 475. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.012. |
| [31] |
FREEMERMAN AJ, JOHNSON AR, SACKS GN, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages: Glucose transporter 1(GLUT1)-mediated glucose metabolism drives a proinflammatory phenotype[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289( 11): 7884- 7896. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.522037. |
| [32] |
PAVLOU S, WANG LX, XU HP, et al. Higher phagocytic activity of thioglycollate-elicited peritoneal macrophages is related to metabolic status of the cells[J]. J Inflamm(Lond), 2017, 14: 4. DOI: 10.1186/s12950-017-0151-x. |
| [33] |
WCULEK SK, DUNPHY G, HERAS-MURILLO I, et al. Metabolism of tissue macrophages in homeostasis and pathology[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2022, 19( 3): 384- 408. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-021-00791-9. |
| [34] |
KOO SJ, GARG NJ. Metabolic programming of macrophage functions and pathogens control[J]. Redox Biol, 2019, 24: 101198. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101198. |
| [35] |
LIU ZJ, LE YF, CHEN H, et al. Role of PKM2-mediated immunometabolic reprogramming on development of cytokine storm[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 748573. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.748573. |
| [36] |
PALSSON-MCDERMOTT EM, CURTIS AM, GOEL G, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates Hif-1α activity and IL-1β induction and is a critical determinant of the Warburg effect in LPS-activated macrophages[J]. Cell Metab, 2015, 21( 1): 65- 80. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.12.005. |
| [37] |
MEOLI L, GUPTA NK, SAEIDI N, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and gastric bypass surgery regulate serum and hepatic levels of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme M2[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 315( 4): E613- E621. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00296.2017. |
| [38] |
ZHAO P, HAN SN, ARUMUGAM S, et al. Digoxin improves steatohepatitis with differential involvement of liver cell subsets in mice through inhibition of PKM2 transactivation[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2019, 317( 4): G387- G397. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00054.2019. |
| [39] |
ALQURAISHI M, PUCKETT DL, ALANI DS, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2: A simple molecule with complex functions[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2019, 143: 176- 192. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.08.007. |
| [40] |
WANG Q, BU QF, LIU M, et al. XBP1-mediated activation of the STING signalling pathway in macrophages contributes to liver fibrosis progression[J]. JHEP Rep, 2022, 4( 11): 100555. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100555. |
| [41] |
YUAN YD, JIANG SJ, ZHANG YL. Research progress in the treatment of metabolic related diseases with Wendan decoction and its modified formulas[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2025, 41( 3): 328- 333. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2025.03.021. |
| [42] |
ZHOU L, ZHAO J, MA K, et al. Targeting immune cellular populations and transcription factors: unraveling the therapeutic potential of JQF for NAFLD[J]. Front Immunol, 2025, 15: 1445924. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1445924. |
| [43] |
NATI M, CHUNG KJ, CHAVAKIS T. The role of innate immune cells in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Innate Immun, 2022, 14( 1): 31- 41. DOI: 10.1159/000518407. |
| [44] |
ZHOU JG, SUN L, LIU L, et al. Hepatic macrophage targeted siRNA lipid nanoparticles treat non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Control Release, 2022, 343: 175- 186. DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.01.038. |
| [45] |
YANG W, YAN XX, CHEN R, et al. Smad4 deficiency in hepatocytes attenuates NAFLD progression via inhibition of lipogenesis and macrophage polarization[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2025, 16( 1): 58. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07376-8. |



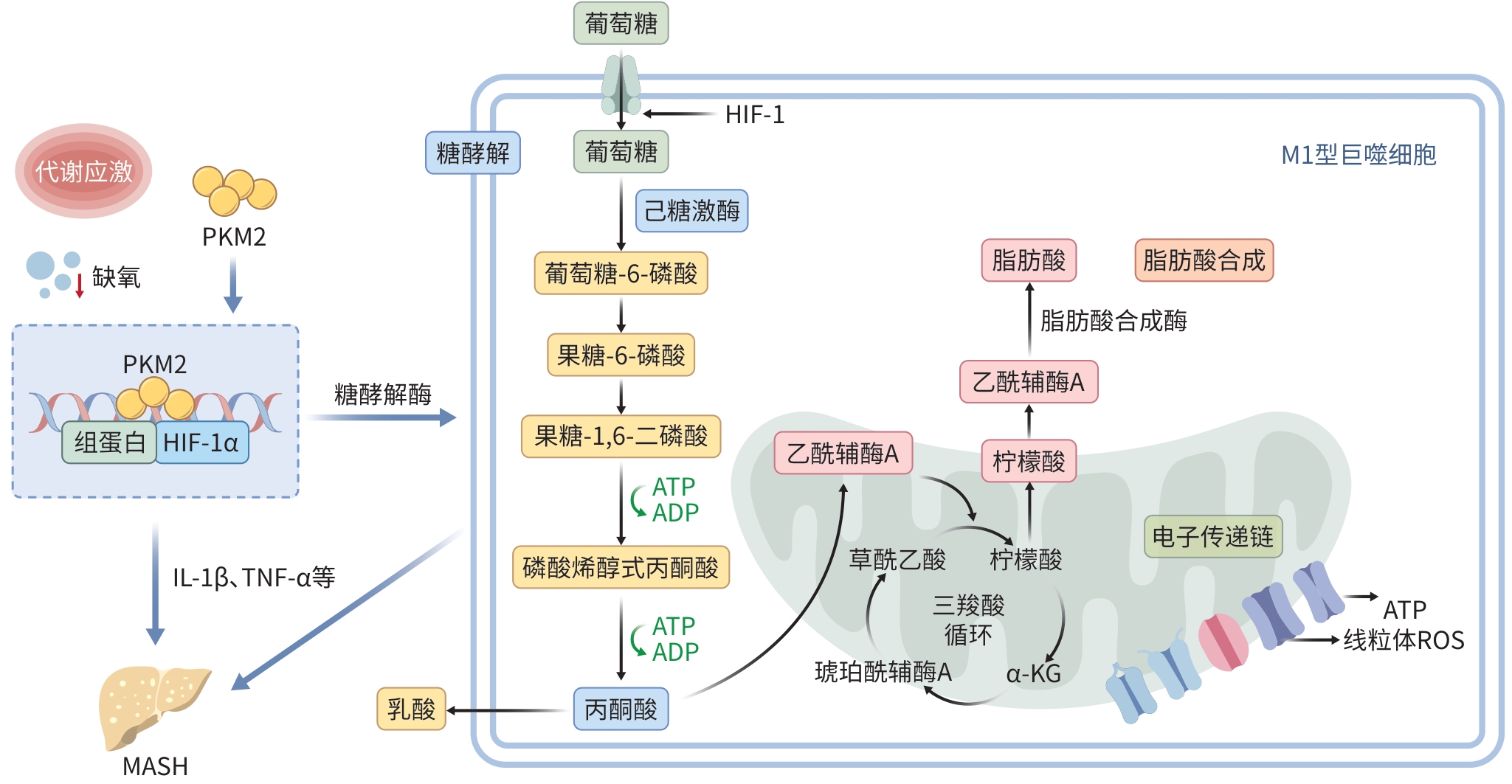




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: