| [1] |
FRIEDMAN SL, NEUSCHWANDER-TETRI BA, RINELLA M, et al. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24( 7): 908- 922. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9. |
| [2] |
TANASE DM, GOSAV EM, COSTEA CF, et al. The intricate relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM), insulin resistance(IR), and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020, 2020: 3920196. DOI: 10.1155/2020/3920196. |
| [3] |
POUWELS S, SAKRAN N, GRAHAM Y, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2022, 22( 1): 63. DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-00980-1. |
| [4] |
GAITONDE DY, COOK DL, RIVERA IM. Chronic kidney disease: Detection and evaluation[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2017, 96( 12): 776- 783.
|
| [5] |
BENOIT SW, CICCIA EA, DEVARAJAN P. Cystatin C as a biomarker of chronic kidney disease: Latest developments[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2020, 20( 10): 1019- 1026. DOI: 10.1080/14737159.2020.1768849. |
| [6] |
NIU YX, ZHANG WW, ZHANG HM, et al. Serum creatinine levels and risk of nonalcohol fatty liver disease in a middle-aged and older Chinese population: A cross-sectional analysis[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2022, 38( 2): e3489. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.3489. |
| [7] |
HWANG JA, SONG Y, SHIN J, et al. Changes in mortality according to creatinine/cystatin C ratio in chronic kidney disease and non-chronic kidney disease patients[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2022, 9: 810901. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.810901. |
| [8] |
SHI JL, WU YF, ZHU SY, et al. The association between serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: Insights from NHANES[J]. Rev Cardiovasc Med, 2023, 24( 9): 275. DOI: 10.31083/j.rcm2409275. |
| [9] |
BEDOGNI G, BELLENTANI S, MIGLIOLI L, et al. The Fatty Liver Index: A simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2006, 6( 1): 33. DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-6-33. |
| [10] |
GOLABI P, GERBER L, PAIK JM, et al. Contribution of sarcopenia and physical inactivity to mortality in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. JHEP Rep, 2020, 2( 6): 100171. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100171. |
| [11] |
LIU CF, CHIEN LW. Predictive role of neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio(NPAR) in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and advanced liver fibrosis in nondiabetic US adults: Evidence from NHANES 2017-2018[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15( 8): 1892. DOI: 10.3390/nu15081892. |
| [12] |
OSAKA T, HAMAGUCHI M, HASHIMOTO Y, et al. Decreased the creatinine to cystatin C ratio is a surrogate marker of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2018, 139: 52- 58. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.025. |
| [13] |
LI SB, LU J, GU G, et al. Serum creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio in the progression monitoring of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 664100. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.664100. |
| [14] |
KITAGO M, SEINO S, SHINKAI S, et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations of creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio with sarcopenia parameters in older adults[J]. J Nutr Health Aging, 2023, 27( 11): 946- 952. DOI: 10.1007/s12603-023-2029-3. |
| [15] |
TABARA Y, KOHARA K, OKADA Y, et al. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio as a marker of skeletal muscle mass in older adults: J-SHIPP study[J]. Clin Nutr, 2020, 39( 6): 1857- 1862. DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.07.027. |
| [16] |
MIKAMI K, ENDO T, SAWADA N, et al. Association of serum creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio with skeletal muscle mass and strength in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Iwaki Health Promotion Project[J]. J Clin Biochem Nutr, 2022, 70( 3): 273- 282. DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.21-61. |
| [17] |
CHUNG GE, KIM MJ, YIM JY, et al. Sarcopenia is significantly associated with presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Obes Metab Syndr, 2019, 28( 2): 129- 138. DOI: 10.7570/jomes.2019.28.2.129. |
| [18] |
LUO YF, LIN H. Inflammation initiates a vicious cycle between obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2021, 9( 1): 59- 73. DOI: 10.1002/iid3.391. |
| [19] |
UTZSCHNEIDER KM, KAHN SE. The role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2006, 91( 12): 4753- 4761. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2006-0587. |
| [20] |
LIU ZJ, ZHU CF. Causal relationship between insulin resistance and sarcopenia[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2023, 15( 1): 46. DOI: 10.1186/s13098-023-01022-z. |
| [21] |
CAPEL F, PINEL A, WALRAND S. Accumulation of intramuscular toxic lipids, a link between fat mass accumulation and sarcopenia[J]. Ocl, 2019, 26: 24. DOI: 10.1051/ocl/2019023. |
| [22] |
FRANK AP, de SOUZA SANTOS R, PALMER BF, et al. Determinants of body fat distribution in humans may provide insight about obesity-related health risks[J]. J Lipid Res, 2019, 60( 10): 1710- 1719. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R086975. |
| [23] |
de PAOLI M, ZAKHARIA A, WERSTUCK GH. The role of estrogen in insulin resistance: A review of clinical and preclinical data[J]. Am J Pathol, 2021, 191( 9): 1490- 1498. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.05.011. |
| [24] |
GERACI A, CALVANI R, FERRI E, et al. Sarcopenia and menopause: The role of estradiol[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2021, 12: 682012. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.682012. |
| [25] |
JEONG HG, PARK H. Metabolic disorders in menopause[J]. Metabolites, 2022, 12( 10): 954. DOI: 10.3390/metabo12100954. |
| [26] |
DAM TV, DALGAARD LB, RINGGAARD S, et al. Transdermal estrogen therapy improves gains in skeletal muscle mass after 12 weeks of resistance training in early postmenopausal women[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 11: 596130. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.596130. |



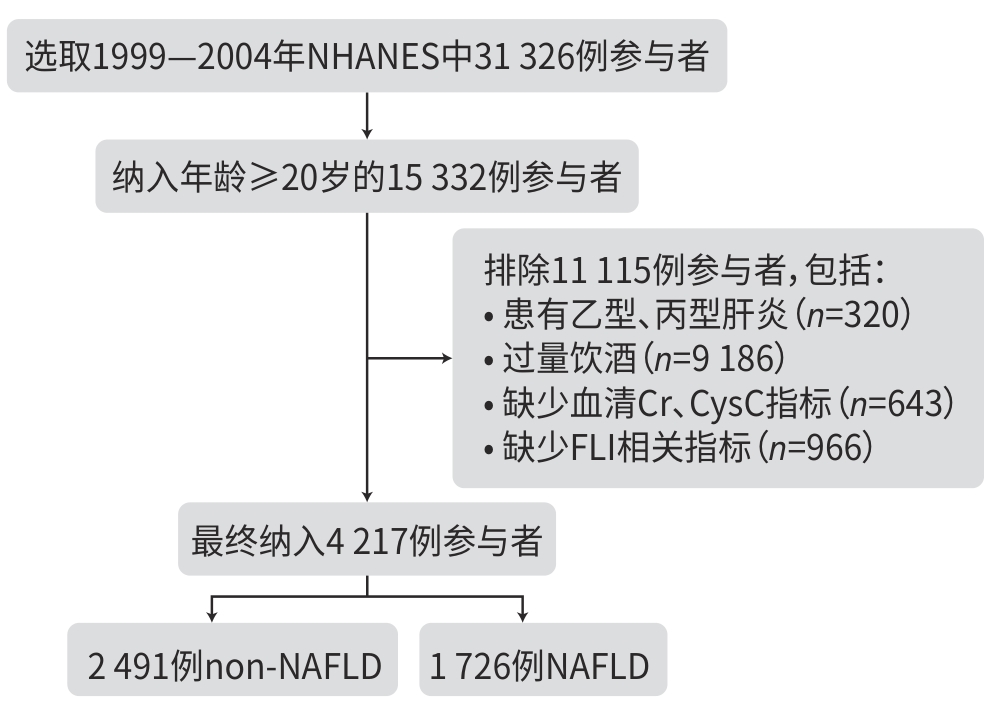




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
