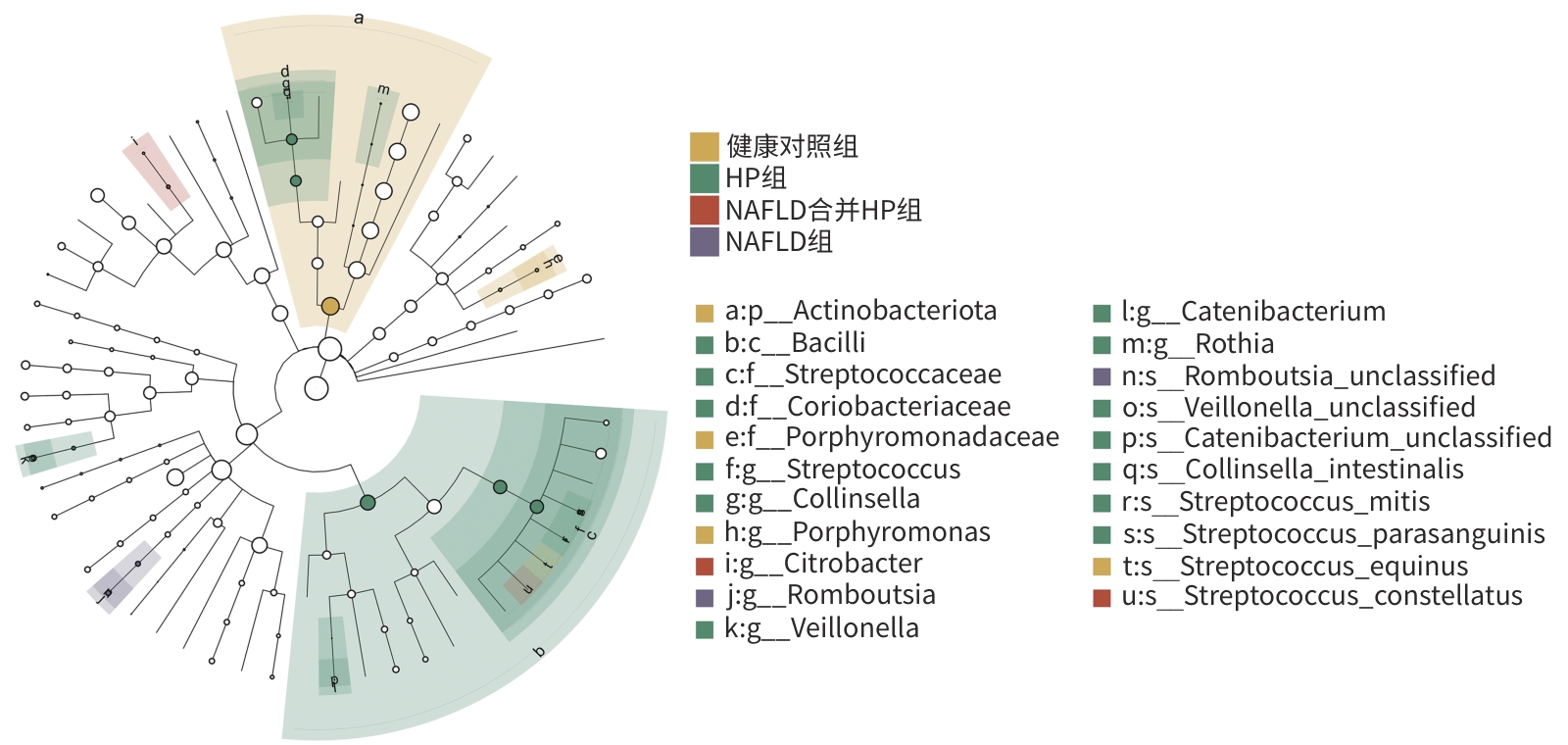
| [1] |
FANG J, YU CH, LI XJ, et al. Gut dysbiosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 997018. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.997018. |
| [2] |
ZHANG YB, GUO GY, ZHENG CH, et al. Research progress in association between Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome and its effect on occurrence and development of metabolic syndrome[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2024, 50( 6): 1757- 1762. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240631. |
| [3] |
ABO-AMER YE, SABAL A, AHMED R, et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) in a developing country: A cross-sectional study[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2020, 13: 619- 625. DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S237866. |
| [4] |
OKUSHIN K, TSUTSUMI T, IKEUCHI K, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and liver diseases: Epidemiology and insights into pathogenesis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 32): 3617- 3625. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i32.3617. |
| [5] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated(non-alcoholic) fatty liver disease(Version 2024)[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2024, 27( 4): 494- 510.
中华医学会肝病学分会. 代谢相关(非酒精性)脂肪性肝病防治指南(2024年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2024, 27( 4): 494- 510.
|
| [6] |
KONING M, HERREMA H, NIEUWDORP M, et al. Targeting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via gut microbiome-centered therapies[J]. Gut Microbes, 2023, 15( 1): 2226922. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2226922. |
| [7] |
ZHANG DY, WANG Q, BAI FH. Bidirectional relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Insights from a comprehensive meta-analysis[J]. Front Nutr, 2024, 11: 1410543. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1410543. |
| [8] |
MANTOVANI A, LANDO MG, BORELLA N, et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: An updated meta-analysis[J]. Liver Int, 2024, 44( 7): 1513- 1525. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15925. |
| [9] |
THURSBY E, JUGE N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota[J]. Biochem J, 2017, 474( 11): 1823- 1836. DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160510. |
| [10] |
LEVY M, KOLODZIEJCZYK AA, THAISS CA, et al. Dysbiosis and the immune system[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2017, 17( 4): 219- 232. DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.7. |
| [11] |
BOURSIER J, MUELLER O, BARRET M, et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63( 3): 764- 775. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28356. |
| [12] |
MAVILIA-SCRANTON MG, WU GY, DHARAN M. Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on the pathogenesis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2023, 11( 3): 670- 674. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00362. |
| [13] |
GAO JJ, ZHANG Y, GERHARD M, et al. Association between gut microbiota and Helicobacter pylori-related gastric lesions in a high-risk population of gastric cancer[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2018, 8: 202. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00202. |
| [14] |
NABAVI-RAD A, SADEGHI A, ASADZADEH AGHDAEI H, et al. The double-edged sword of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota structure in Helicobacter pylori management[J]. Gut Microbes, 2022, 14( 1): 2108655. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2108655. |
| [15] |
DU LJ, CHEN BR, CHENG FL, et al. Effects of Helicobacter pylori therapy on gut microbiota: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dig Dis, 2024, 42( 1): 102- 112. DOI: 10.1159/000527047. |
| [16] |
WANG YH, HUANG Y. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum supplementation to standard triple therapy on Helicobacter pylori eradication and dynamic changes in intestinal flora[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2014, 30( 3): 847- 853. DOI: 10.1007/s11274-013-1490-2. |
| [17] |
WEISS G, FORSTER S, IRVING A, et al. Helicobacter pylori VacA suppresses Lactobacillus acidophilus-induced interferon beta signaling in macrophages via alterations in the endocytic pathway[J]. mBio, 2013, 4( 3): e00609-12. DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00609-12. |
| [18] |
AHN SB, JUN DW, KANG BK, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of a multispecies probiotic mixture in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 5688. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42059-3. |
| [19] |
den BESTEN G, van EUNEN K, GROEN AK, et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism[J]. J Lipid Res, 2013, 54( 9): 2325- 2340. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R036012. |
| [20] |
YOON SJ, YU JS, MIN BH, et al. Bifidobacterium-derived short-chain fatty acids and indole compounds attenuate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut-liver axis[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1129904. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1129904. |
| [21] |
BLAAK EE, CANFORA EE, THEIS S, et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health[J]. Benef Microbes, 2020, 11( 5): 411- 455. DOI: 10.3920/BM2020.0057. |
| [22] |
MBAYE B, MAGDY WASFY R, BORENTAIN P, et al. Increased fecal ethanol and enriched ethanol-producing gut bacteria Limosilactobacillus fermentum, Enterocloster bolteae, Mediterraneibacter gnavus and Streptococcus mutans in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13: 1279354. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1279354. |
| [23] |
CROST EH, COLETTO E, BELL A, et al. Ruminococcus gnavus: Friend or foe for human health[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2023, 47( 2): fuad014. DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuad014. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: