| [1] |
ANDO R, SHIRAKI Y, MIYAI Y, et al. Meflin is a marker of pancreatic stellate cells involved in fibrosis and epithelial regeneration in the pancreas[J]. J Pathol, 2024, 262( 1): 61- 75. DOI: 10.1002/path.6211. |
| [2] |
KONG FY, PAN YY, WU D. Activation and regulation of pancreatic stellate cells in chronic pancreatic fibrosis: A potential therapeutic approach for chronic pancreatitis[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12( 1): 108. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12010108. |
| [3] |
REBELO R, XAVIER CPR, GIOVANNETTI E, et al. Fibroblasts in pancreatic cancer: Molecular and clinical perspectives[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2023, 29( 6): 439- 453. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.03.002. |
| [4] |
CUI LZ, ZHANG XW, ZHAI Y, et al. Promotion effect of chemokine CCL19-induced macrophage M1 polarization on chronic pancreatitis in mice and its mechanism[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2024, 50( 6): 1587- 1596. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240612. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
JI XD, GONG B, LI XJ, et al. Application of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of pancreatic fibrosis: Clinical strategies and research advances[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 9): 2258- 2264. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.034. |
| [7] |
WANG ZF, DONG S, ZHOU WC. Pancreatic stellate cells: Key players in pancreatic health and diseases(Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2024, 30( 1): 109. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13233. |
| [8] |
NG B, VISWANATHAN S, WIDJAJA AA, et al. IL11 activates pancreatic stellate cells and causes pancreatic inflammation, fibrosis and atrophy in a mouse model of pancreatitis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 7): 3549. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23073549. |
| [9] |
SUN L, ZHENG MF, GAO YH, et al. Retinoic acid signaling pathway in pancreatic stellate cells: Insight into the anti-fibrotic effect and mechanism[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, 967: 176374. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176374. |
| [10] |
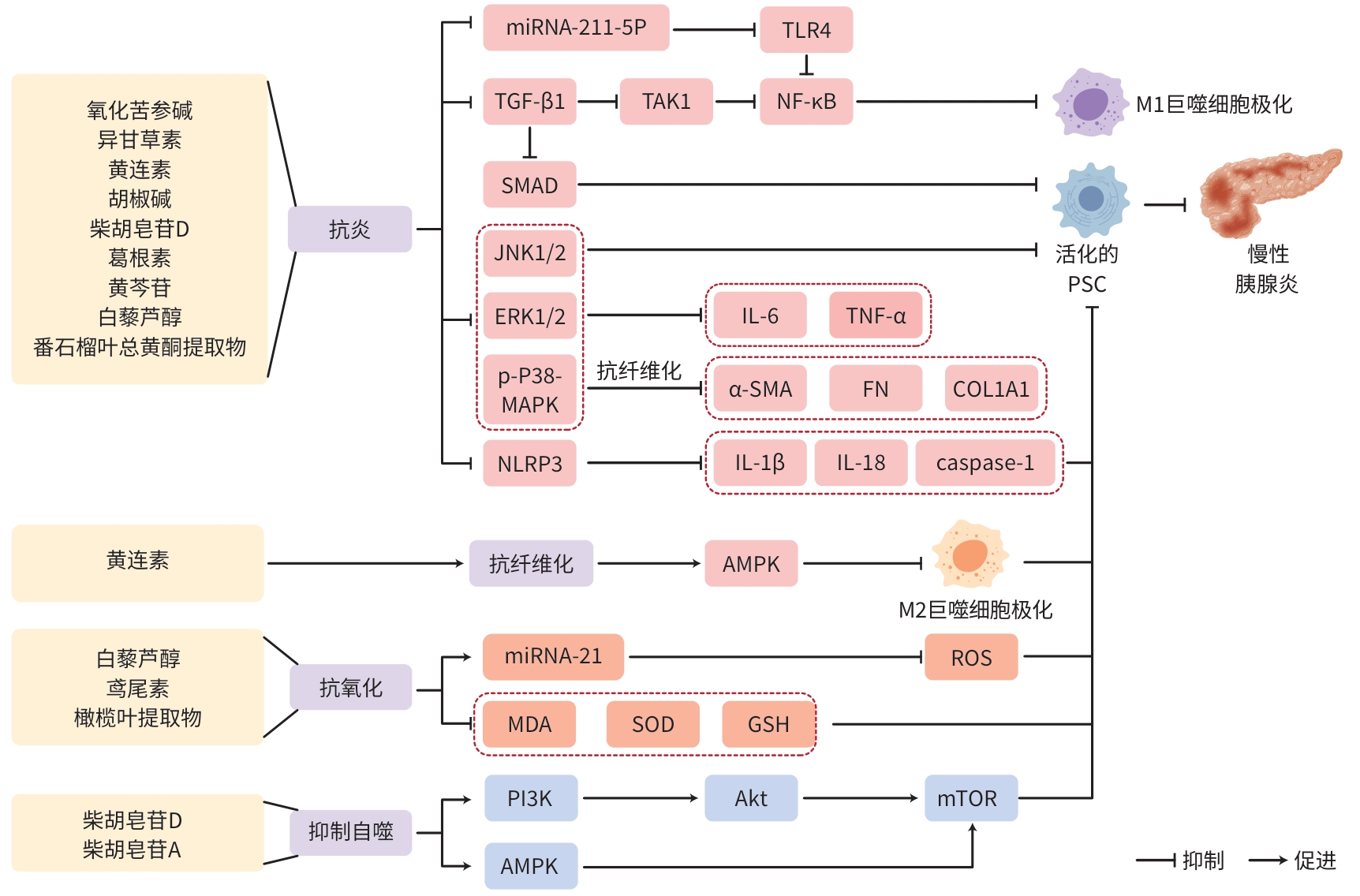
WANG LJ, HE L, HAO L, et al. Isoliquiritigenin ameliorates caerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis by inhibiting the activation of PSCs and pancreatic infiltration of macrophages[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24( 17): 9667- 9681. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15498. |
| [11] |
TSANG SW, ZHANG HJ, LIN ZS, et al. Anti-fibrotic effect of trans-resveratrol on pancreatic stellate cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2015, 71: 91- 97. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.02.013. |
| [12] |
BANSOD S, DOIJAD N, GODUGU C. Berberine attenuates severity of chronic pancreatitis and fibrosis via AMPK-mediated inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signaling and M2 polarization[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2020, 403: 115162. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115162. |
| [13] |
CHOI JW, LEE SK, KIM MJ, et al. Piperine ameliorates the severity of fibrosis via inhibition of TGF-β/SMAD signaling in a mouse model of chronic pancreatitis[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 20( 4): 3709- 3718. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10635. |
| [14] |
CHOI JW, SHIN JY, ZHOU ZQ, et al. Stem bark of Fraxinus rhynchophylla ameliorates the severity of pancreatic fibrosis by regulating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. J Investig Med, 2022, 70( 5): 1285- 1292. DOI: 10.1136/jim-2021-002169. |
| [15] |
KWEON B, KIM DU, OH JY, et al. Catechin hydrate ameliorates cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis via the inactivation of TGF-β/Smad2 signaling[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2023, 28( 5): 208. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13095. |
| [16] |
LI CX, CUI LH, ZHANG LQ, et al. Saikosaponin D attenuates pancreatic injury through suppressing the apoptosis of acinar cell via modulation of the MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 735079. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.735079. |
| [17] |
ZENG XP, ZENG JH, LIN X, et al. Puerarin ameliorates caerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis via inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 686992. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.686992. |
| [18] |
FAN JW, DUAN LF, WU N, et al. Baicalin ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of pancreatic stellate cells in mice with chronic pancreatitis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 11: 607133. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.607133. |
| [19] |
FAN JW, XU XF, XIN JQ, et al. Baicalin attenuates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1/TAK-NF-κB signaling pathway in chronic pancreatitis mice[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2020, 36( 2): 268- 275. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2020.02.012. |
| [20] |
ZHANG GX, TANG LM, LIU HB, et al. Psidium guajava flavonoids prevent NLRP3 inflammasome activation and alleviate the pancreatic fibrosis in a chronic pancreatitis mouse model[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2021, 49( 8): 2001- 2015. DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X21500944. |
| [21] |
WANG MX, ZHANG GX, LIU HB, et al. Effect of total flavonoids from Psidium guajava leaves on pancreatic fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis mice[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2018, 24( 10): 175- 180. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20181039. |
| [22] |
LI RY, XIANG XH, ZHANG B, et al. Oxymatrine participates in regulation of TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory response pathway via miRNA-211-5p in PSCs[J]. Drug Eval Res, 2018, 41( 4): 540- 546. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2018.04.007. |
| [23] |
YAN B, CHENG L, JIANG ZD, et al. Resveratrol inhibits ROS-promoted activation and glycolysis of pancreatic stellate cells via suppression of miR-21[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 1346958. DOI: 10.1155/2018/1346958. |
| [24] |
REN YF, ZHANG J, WANG MZ, et al. Identification of irisin as a therapeutic agent that inhibits oxidative stress and fibrosis in a murine model of chronic pancreatitis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 126: 110101. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110101. |
| [25] |
ROMEH GH, EL-SAFTY FEA, EL-MEHI AE, et al. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties of olive leaf extract protect against L-arginine induced chronic pancreatitis in the adult male albino rat[J]. Anat Cell Biol, 2022, 55( 2): 205- 216. DOI: 10.5115/acb.21.187. |
| [26] |
CUI LH, LI CX, ZHUO YZ, et al. Saikosaponin d ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting autophagy of pancreatic stellate cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2019, 300: 18- 26. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.01.005. |
| [27] |
CUI LH, LI CX, ZHUO YZ, et al. Saikosaponin A inhibits the activation of pancreatic stellate cells by suppressing autophagy and the NLRP3 inflammasome via the AMPK/mTOR pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 128: 110216. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110216. |
| [28] |
HU Y, TENG CY, YU SM, et al. Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide regulates gut microbiota of chronic pancreatitis in mice[J]. AMB Express, 2017, 7( 1): 39. DOI: 10.1186/s13568-017-0341-1. |
| [29] |
LI KK, ZHUO C, TENG CY, et al. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on chronic pancreatitis and intestinal microbiota in mice[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2016, 93: 904- 912. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.09.029. |
| [30] |
ZHANG Y, ZHANG WQ, LIU XY, et al. Immune cells and immune cell-targeted therapy in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1151103. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1151103. |
| [31] |
PENG C, TU GP, YU L, et al. Murine chronic pancreatitis model induced by partial ligation of the pancreatic duct encapsulates the profile of macrophage in human chronic pancreatitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 840887. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.840887. |
| [32] |
KUO TL, CHENG KH, SHAN YS, et al. β-catenin-activated autocrine PDGF/Src signaling is a therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9( 2): 324- 336. DOI: 10.7150/thno.28201. |
| [33] |
WU N, XU XF, XIN JQ, et al. The effects of nuclear factor-kappa B in pancreatic stellate cells on inflammation and fibrosis of chronic pancreatitis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25( 4): 2213- 2227. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16213. |
| [34] |
LI CX, CUI LH, ZHANG LQ, et al. Role of NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome in the activation of pancreatic stellate cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2021, 404( 2): 112634. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112634. |
| [35] |
CUI LH, LI CX, ZHANG GX, et al. S1P/S1PR2 promote pancreatic stellate cell activation and pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis by regulating autophagy and the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2023, 380: 110541. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110541. |
| [36] |
XUE R, WANG JX, YANG LX, et al. Coenzyme Q10 ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis via the ROS-triggered mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 8039694. DOI: 10.1155/2019/8039694. |
| [37] |
SRINIVASAN MP, BHOPALE KK, CARACHEO AA, et al. Exposure to binge ethanol and fatty acid ethyl esters exacerbates chronic ethanol-induced pancreatic injury in hepatic alcohol dehydrogenase-deficient Deer mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2022, 322( 3): G327- G345. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00263.2021. |
| [38] |
KLIONSKY DJ, PETRONI G, AMARAVADI RK, et al. Autophagy in major human diseases[J]. EMBO J, 2021, 40( 19): e108863. DOI: 10.15252/embj.2021108863. |
| [39] |
LI CX, CUI LH, ZHUO YZ, et al. Inhibiting autophagy promotes collagen degradation by regulating matrix metalloproteinases in pancreatic stellate cells[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 208: 276- 283. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.07.049. |
| [40] |
LIU L, ZHANG T, SUI YH, et al. Gut microbiota affects pancreatic fibrotic progression through immune modulation in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Microb Pathog, 2023, 177: 106035. DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106035. |
| [41] |
PAN LL, REN ZN, YANG J, et al. Gut microbiota controls the development of chronic pancreatitis: A critical role of short-chain fatty acids-producing Gram-positive bacteria[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2023, 13( 10): 4202- 4216. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.08.002. |
| [42] |
FANG J. Effect of the treatment of smoothing liver, tonifying spleen and dredging collaterals on Smad signal pathway of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic fibrosis[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of TCM, 2018.
方菁. 加味健脾疏肝通络方调控慢性胰腺炎胰腺纤维化Smad相关蛋白的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江中医药大学, 2018.
|
| [43] |
XU XF, JIANG TT, LIU F, et al. Effect of DaChaiHu Decoction on pancreatic fibrosis induced by DBTC combined with alcohol and the mechanism of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Chin J Appl Physiol, 2016, 32( 5): 444- 448, 482. DOI: 10.13459/j.cnki.cjap.2016.05.015. |
| [44] |
DUAN LF, XU XF, ZHU LJ, et al. Dachaihu decoction ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting macrophage infiltration in chronic pancreatitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23( 40): 7242- 7252. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7242. |
| [45] |
LIANG XQ, WANG YF, ZHANG XL, et al. Effects of Dahuang Danshen decoction on the expressions of TGF-β 1, PDGF-BB, TGF-β 1 mRNA and PDGF-BB mRNA in rats with pancreatic fibrosis[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2014, 55( 15): 1331- 1334. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2014.15.019. |
| [46] |
ZHANG SK, CUI NQ, ZHUO YZ, et al. Modified xiaochaihu decoction promotes collagen degradation and inhibits pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis rats[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2020, 26( 8): 599- 603. DOI: 10.1007/s11655-017-2413-0. |
| [47] |
CUI LH, LI CX, SHANG Y, et al. Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang decoction ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis via JNK/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 679557. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.679557. |
| [48] |
ZHANG GX, ZHAO XM, CAI J, et al. XCHT alleviates the pancreatic fibrosis via VDR/NLRP3 signaling pathway in a mouse model of CP[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 300: 115689. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115689. |
| [49] |
LIANG XQ, HAN M, ZHANG XL, et al. Dahuang Danshen decoction inhibits pancreatic fibrosis by regulating oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 6629729. DOI: 10.1155/2021/6629729. |
| [50] |
GAO LJ, YAO L, GUAN L, et al. Effects of yitai compound on endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic fibrosis[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2023, 41( 3): 198- 202, 277- 280. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2023.03.043. |
| [51] |
JIN GH, HONG WL, GUO YY, et al. Molecular mechanism of pancreatic stellate cells activation in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11( 6): 1505- 1515. DOI: 10.7150/jca.38616. |
| [52] |
XU XF, LIU F, XIN JQ, et al. Respective roles of the mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPK) family members in pancreatic stellate cell activation induced by transforming growth factor-β1(TGF-β1)[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 501( 2): 365- 373. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.176. |
| [53] |
ZHENG MF, GAO RP. Vitamin D: A potential star for treating chronic pancreatitis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 902639. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.902639. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: