| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
LIU YX, ZHENG ZB. Understanding the global cancer statistics 2022: Growing cancer burden[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2024, 67( 10): 2274- 2276. DOI: 10.1007/s11427-024-2657-y. |
| [3] |
RUMGAY H, ARNOLD M, FERLAY J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 6): 1598- 1606. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021. |
| [4] |
National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2024 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 5): 893- 918. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240508. 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2024年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 5): 893- 918. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240508. |
| [5] |
LU J, ZHANG XP, ZHONG BY, et al. Management of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumour thrombosis: Comparing east and west[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4( 9): 721- 730. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30178-5. |
| [6] |
DING CM, HOU JF, TAO GW, et al. Early diagnosis and screening of hepatocellular carcinoma[J/OL]. Chin J Hepat Surg(Electronic Edition), 2023, 12( 1): 22- 28. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2023.01.005. |
| [7] |
WANG XP, WANG QX. Alpha-fetoprotein and hepatocellular carcinoma immunity[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 2018: 9049252. DOI: 10.1155/2018/9049252. |
| [8] |
LU QQ, LI J, CAO H, et al. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of Midkine and AFP for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40( 3): BSR20192424. DOI: 10.1042/BSR20192424. |
| [9] |
YU XP, YANG RY, HE ZM, et al. Establishment and validation of nomogram of cancer specific survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with negative alpha fetoprotein based on SEER Database[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2024, 50( 1): 188- 197. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240123. |
| [10] |
LIU YZ, ZHANG J, LIU H, et al. Compensatory upregulation of aldo-keto reductase 1B10 to protect hepatocytes against oxidative stress during hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9( 12): 2730- 2748.
|
| [11] |
SINGAL AG, LLOVET JM, YARCHOAN M, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 78( 6): 1922- 1965. DOI: 10.1097/hep.0000000000000466. |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
MORIGUCHI M, KATAOKA S, ITOH Y. Evolution of systemic treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: Changing treatment strategies and concepts[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2024, 16( 13): 2387. DOI: 10.3390/cancers16132387. |
| [14] |
YUE YX, NING SK, LIU JB, et al. Comparative analysis of the efficacy of interventional therapy and interventional therapy combined with targeted drugs for advanced primary liver cancer[J]. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat, 2021, 28( 10): 788- 791. DOI: 10.16073/j.cnki.cjcpt.2021.10.13. |
| [15] |
FU YL, SHI WX, HUANG S, et al. Comparison of prognostic evaluation and therapeutic guidance value of three clinical staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Guangxi Med Univ, 2018, 35( 12): 1706- 1709. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2018.12.025. |
| [16] |
YE X, LI CY, ZU XY, et al. A large-scale multicenter study validates aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 as a prevalent serum marker for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69( 6): 2489- 2501. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30519. |
| [17] |
HUNG JJ, YEH YC, HSU WH. Prognostic significance of AKR1B10 in patients with resected lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2018, 9( 11): 1492- 1499. DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12863. |
| [18] |
ENDO S, MATSUNAGA T, NISHINAKA T. The role of AKR1B10 in physiology and pathophysiology[J]. Metabolites, 2021, 11( 6): 332. DOI: 10.3390/metabo11060332. |
| [19] |
SHI J, CHEN LX, CHEN Y, et al. Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10(AKR1B10) overexpression in tumors predicts worse overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10( 20): 4892- 4901. DOI: 10.7150/jca.32768. |
| [20] |
QU JY, LI J, ZHANG YM, et al. AKR1B10 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration via the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Cell Biosci, 2021, 11( 1): 163. DOI: 10.1186/s13578-021-00677-3. |
| [21] |
TREVISANI F, GARUTI F, NERI A. Alpha-fetoprotein for diagnosis, prognosis, and transplant selection[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2019, 39( 2): 163- 177. DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1677768. |
| [22] |
EDOO MIA, CHUTTURGHOON VK, WUSU-ANSAH GK, et al. Serum biomarkers AFP, CEA and CA19-9 combined detection for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Iran J Public Health, 2019, 48( 2): 314- 322.
|
| [23] |
WANG Y, XU WL, CHAI XZ. Application of combined serum AFP and AKR1B10 in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2020, 30( 6): 541- 543. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2020.06.002. |
| [24] |
ZHU RP, XIAO J, LUO DT, et al. Serum AKR1B10 predicts the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma—A retrospective single-center study[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 42( 10): 614- 621. DOI: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2019.06.007. |



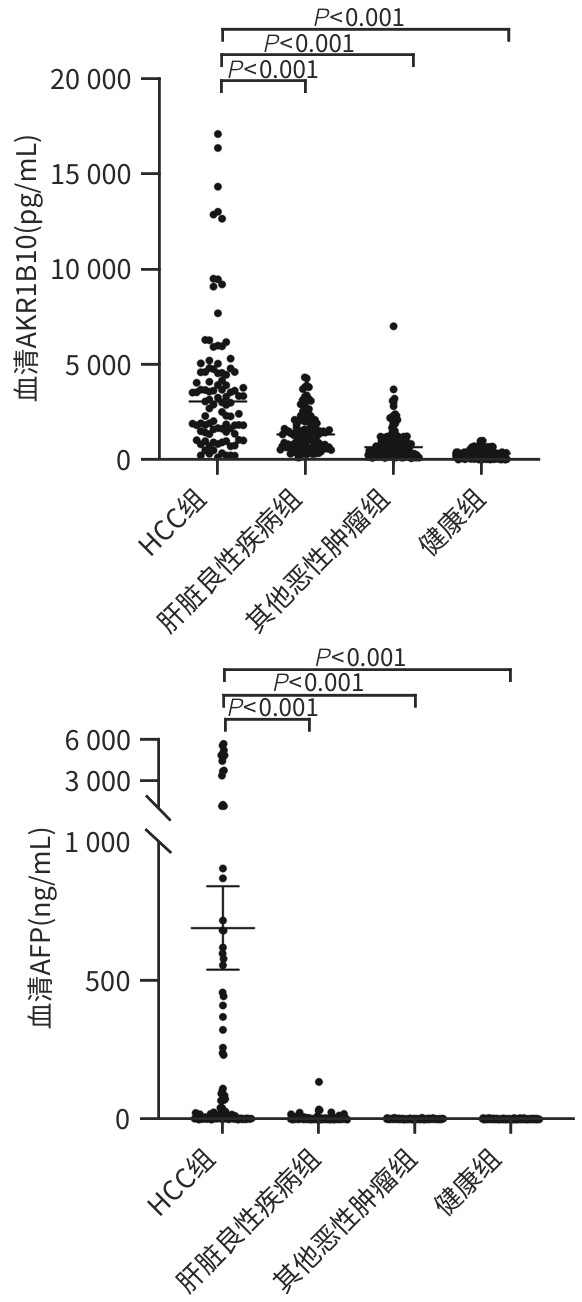




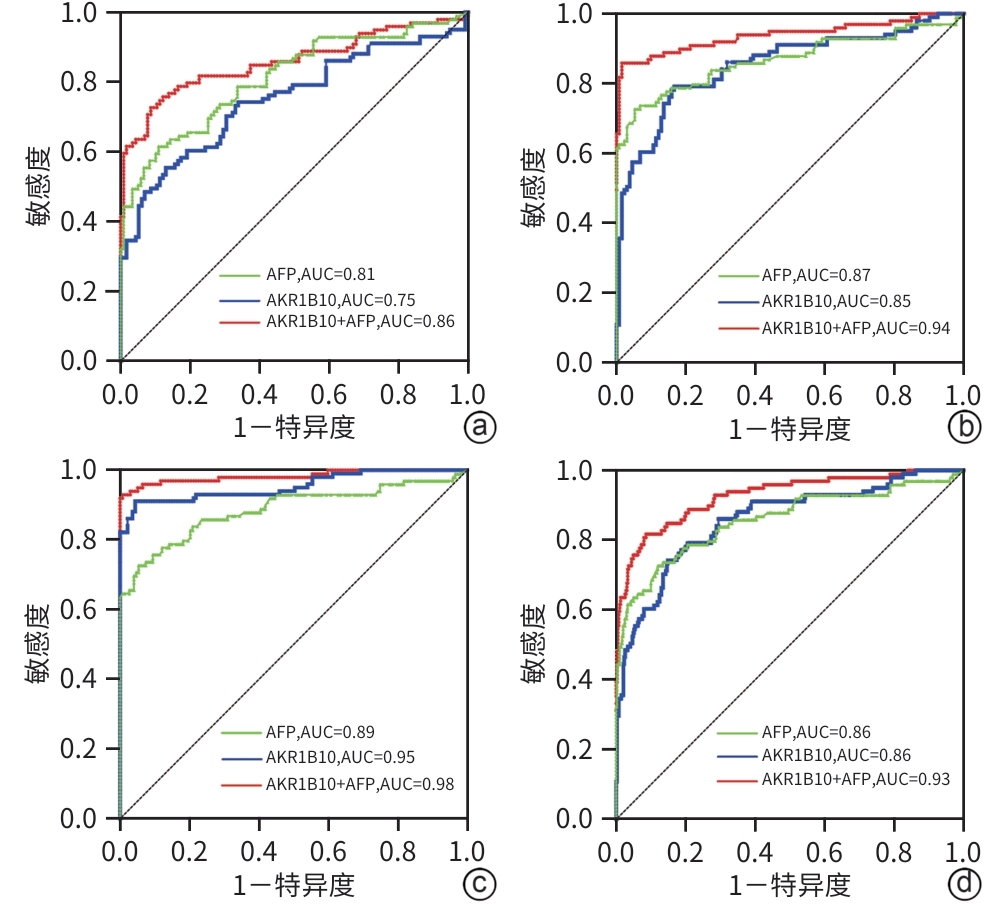
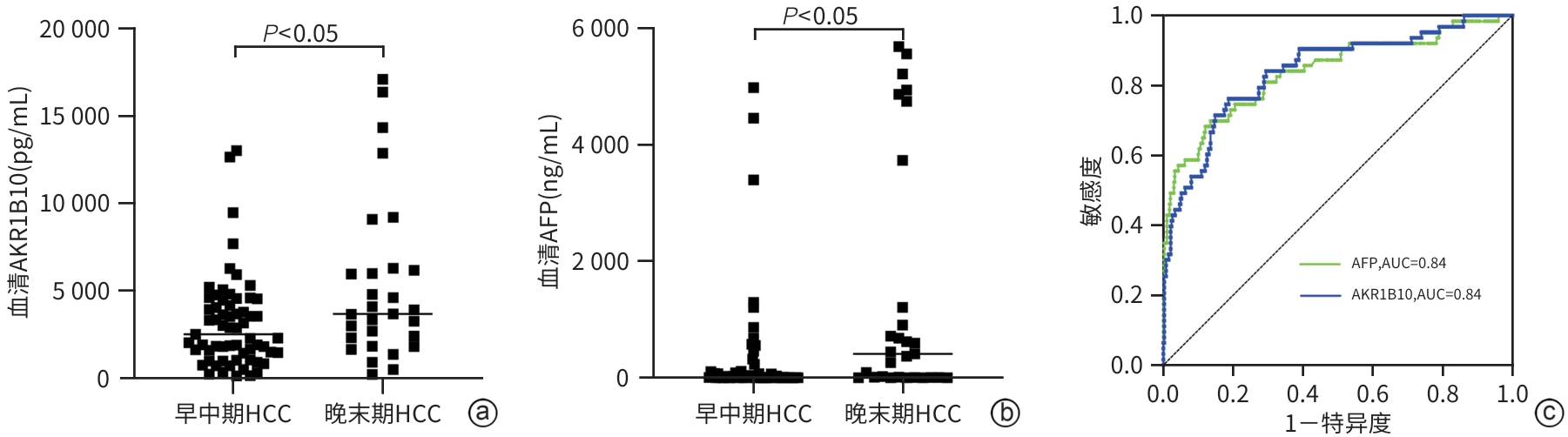
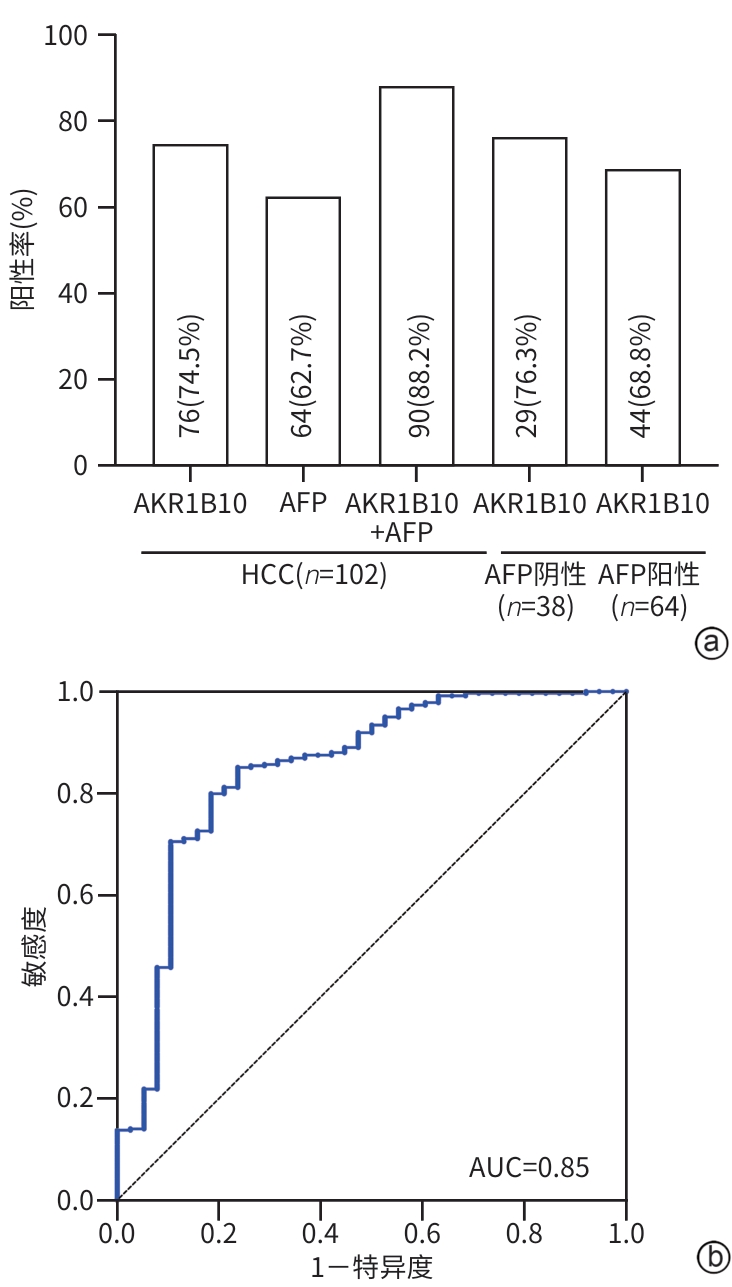
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: