巨噬细胞代谢重编程调控慢加急性肝衰竭的机制与治疗前景
DOI: 10.12449/JCH251230
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:肖滢负责查阅文献,撰写文章;马路园、董世龙负责文章修改;王亚东、赵彩彦负责指导立题,文章审校与修改。
Mechanism and treatment prospects of macrophage metabolic reprogramming in regulating acute-on-chronic liver failure
-
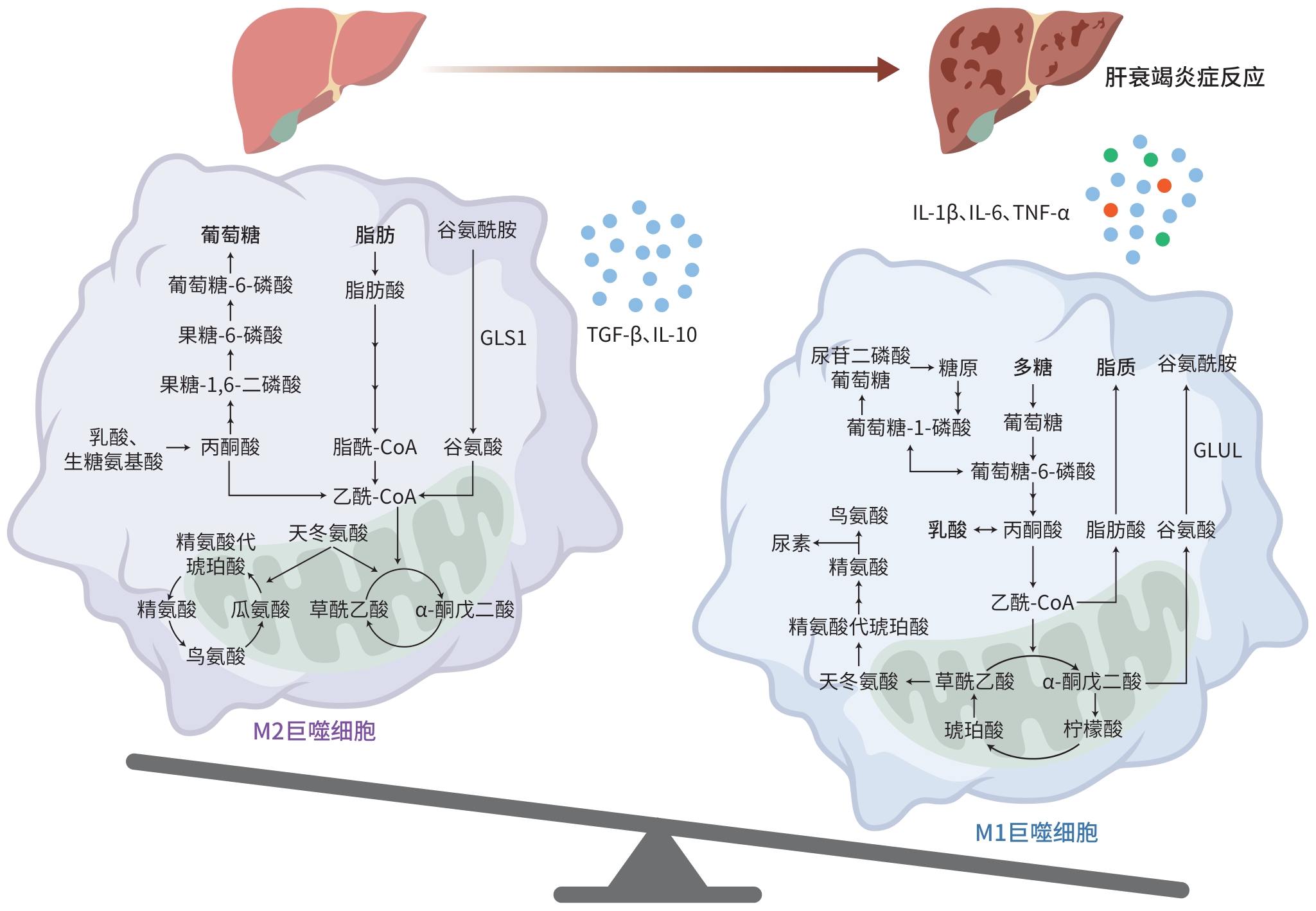
摘要: 代谢重编程是巨噬细胞表型转变的前提和重要标志,不同巨噬细胞表型通过调节炎症反应平衡参与慢加急性肝衰竭(ACLF)发病机制,因此成为ACLF治疗潜在靶位。本综述重点关注ACLF进程中巨噬细胞代谢重编程的变化规律,以及其通过调控能量代谢与免疫炎症介导ACLF严重程度和预后转归的机制,为开发基于巨噬细胞代谢重编程为靶位的ACLF防治策略提供新的思路和方向。Abstract: Metabolic reprogramming is a prerequisite and important marker for macrophage phenotypic transition, and different macrophage phenotypes are involved in the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) by regulating the balance of inflammatory responses, thereby becoming the potential targets for ACLF treatment. This article focuses on the changes in macrophage metabolic reprogramming during ACLF and its mechanism in mediating ACLF severity and prognosis by regulating energy metabolism and immune inflammation, in order to provide new ideas and directions for developing prevention and control strategies for ACLF based on macrophage metabolic reprogramming.
-
Key words:
- Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure /
- Macrophages /
- Inflammation
-
[1] TREBICKA J, HERNAEZ R, SHAWCROSS DL, et al. Recent advances in the prevention and treatment of decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF) and the role of biomarkers[J]. Gut, 2024, 73( 6): 1015- 1024. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330584. [2] PIANO S, MAHMUD N, CARACENI P, et al. Mechanisms and treatment approaches for ACLF[J]. Liver Int, 2025, 45( 3): e15733. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15733. [3] GUILLIAMS M, SCOTT CL. Liver macrophages in health and disease[J]. Immunity, 2022, 55( 9): 1515- 1529. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.08.002. [4] ZHANG Y, WU DS, TIAN XL, et al. From hepatitis B virus infection to acute-on-chronic liver failure: The dynamic role of hepatic macrophages[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2024, 99( 3): e13349. DOI: 10.1111/sji.13349. [5] GAO CC, BAI J, HAN H, et al. The versatility of macrophage heterogeneity in liver fibrosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 968879. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968879. [6] XIAO Y, LU J, XU SY, et al. Metabolic differences among patients with cirrhosis using Q exactive hybrid quadrupole orbitrap mass spectrometry technology[J]. J Proteome Res, 2024, 23( 12): 5352- 5359. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00437. [7] ZHANG IW, CURTO A, LÓPEZ-VICARIO C, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction governs immunometabolism in leukocytes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76( 1): 93- 106. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.08.009. [8] KORF H, du PLESSIS J, van PELT J, et al. Inhibition of glutamine synthetase in monocytes from patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure resuscitates their antibacterial and inflammatory capacity[J]. Gut, 2019, 68( 10): 1872- 1883. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316888. [9] ZHANG Y, TIAN XL, LI JQ, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction affects hepatic immune and metabolic remodeling in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2024, 30( 8): 881- 900. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.881. [10] RAO JH, WANG H, NI M, et al. FSTL1 promotes liver fibrosis by reprogramming macrophage function through modulating the intracellular function of PKM2[J]. Gut, 2022, 71( 12): 2539- 2550. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325150. [11] MA JW, WEI KK, LIU JW, et al. Glycogen metabolism regulates macrophage-mediated acute inflammatory responses[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 1769. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15636-8. [12] CUI YX, CHEN JH, ZHANG Z, et al. The role of AMPK in macrophage metabolism, function and polarisation[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21( 1): 892. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04772-6. [13] HAN ZY, SHEN YH, YAN YQ, et al. Metabolic reprogramming shapes post-translational modification in macrophages[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2025, 102: 101338. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2025.101338. [14] ZHANG Y, TAN WT, WANG XB, et al. Metabolic biomarkers significantly enhance the prediction of HBV-related ACLF occurrence and outcomes[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 5): 1159- 1171. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.011. [15] LIU PS, WANG HP, LI XY, et al. α-ketoglutarate orchestrates macrophage activation through metabolic and epigenetic reprogramming[J]. Nat Immunol, 2017, 18( 9): 985- 994. DOI: 10.1038/ni.3796. [16] YU ZJ, LI JJ, REN ZG, et al. Switching from fatty acid oxidation to glycolysis improves the outcome of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Adv Sci, 2020, 7( 7): 1902996. DOI: 10.1002/advs.201902996. [17] BOSMANS LA, van TIEL CM, AARTS SABM, et al. Myeloid CD40 deficiency reduces atherosclerosis by impairing macrophages’ transition into a pro-inflammatory state[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2023, 119( 5): 1146- 1160. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvac084. [18] LIU PS, CHEN YT, LI XY, et al. CD40 signal rewires fatty acid and glutamine metabolism for stimulating macrophage anti-tumorigenic functions[J]. Nat Immunol, 2023, 24( 3): 452- 462. DOI: 10.1038/s41590-023-01430-3. [19] ZHANG QY, SONG QL, LIU S, et al. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the metabolic programming of GM-CSF-and M-CSF-differentiated mouse macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1230772. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1230772. [20] MAO YX, SHI D, LI G, et al. Citrulline depletion by ASS1 is required for proinflammatory macrophage activation and immune responses[J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82( 3): 527- 541. e 7. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.12.006. [21] YAN JW, HORNG T. Lipid metabolism in regulation of macrophage functions[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2020, 30( 12): 979- 989. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.09.006. [22] YANG Y, NI M, ZONG RB, et al. Targeting Notch1-YAP circuit reprograms macrophage polarization and alleviates acute liver injury in mice[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 15( 5): 1085- 1104. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.01.002. [23] SÁNCHEZ-RODRÍGUEZ MB, TÉLLEZ É, CASULLERAS M, et al. Reduced plasma extracellular vesicle CD5L content in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: Interplay with specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 842996. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.842996. [24] PENG B, LI H, LIU K, et al. Intrahepatic macrophage reprogramming associated with lipid metabolism in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21( 1): 419. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04294-1. [25] MAHESHWARI D, KUMAR D, JAGDISH RK, et al. Bioenergetic failure drives functional exhaustion of monocytes in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 856587. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.856587. [26] MAIWALL R, BAJPAI M, CHOUDHURY AK, et al. Therapeutic plasma-exchange improves systemic inflammation and survival in acute-on-chronic liver failure: A propensity-score matched study from AARC[J]. Liver Int, 2021, 41( 5): 1083- 1096. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14806. [27] LI ZH, WANG JY, LI XL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-regulated miRNA-mRNA landscape in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Genomics, 2023, 115( 6): 110737. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110737. [28] GAO YH, MI NN, WU WX, et al. Transfer of inflammatory mitochondria via extracellular vesicles from M1 macrophages induces ferroptosis of pancreatic beta cells in acute pancreatitis[J]. J Extracell Vesicles, 2024, 13( 2): e12410. DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12410. [29] XUE JH, CHEN F, WANG J, et al. Emodin protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibiting activation of the p38 MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2015, 35( 4): 1557- 1570. DOI: 10.1159/000373971. -



 PDF下载 ( 604 KB)
PDF下载 ( 604 KB)

 下载:
下载:


