线粒体功能紊乱在代谢相关脂肪性肝病中的作用机制及中医药干预研究现状
DOI: 10.12449/JCH251224
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王丹主要负责设计论文框架,撰写论文;张金雪、苏李宁负责查阅文献;刘俊宏、李亚静、赖学倩负责研究选题,终审论文;李红梅、徐冰蕊负责修订论文。
Mechanism of action of mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic associated fatty liver disease and the current status of research on traditional Chinese medicine
-
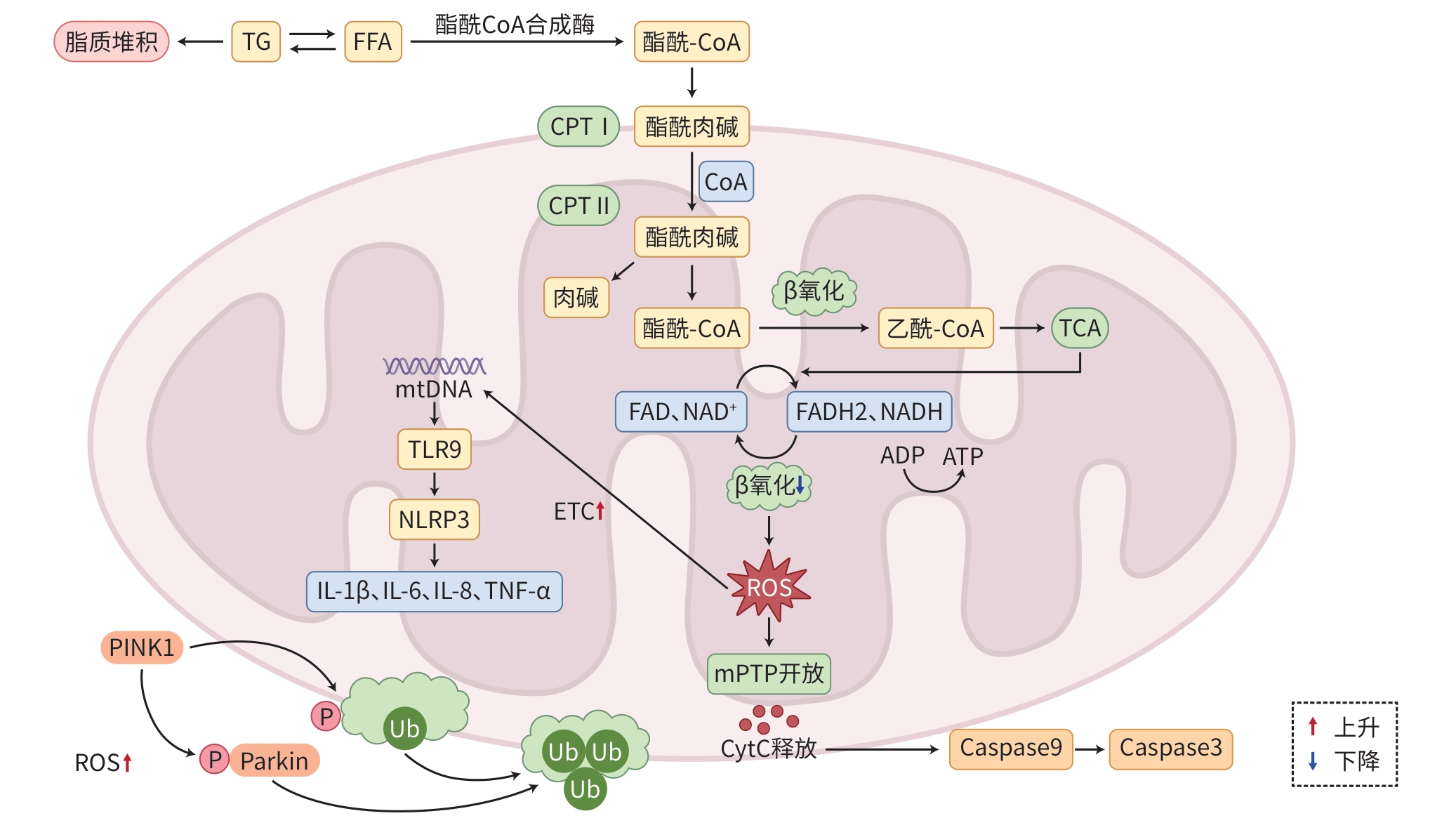
摘要: 代谢相关脂肪性肝病(MAFLD)是一种与代谢紊乱有关的慢性肝病,其发病与肝细胞内脂肪大量堆积引起的脂毒性密切相关。近年研究表明,线粒体功能紊乱是MAFLD发病的重要机制,涉及线粒体氧化应激、线粒体自噬异常、线粒体凋亡异常和线粒体脂质代谢异常等一系列病理变化。中医药基于整体观念和辨证论治两大基本特点,在MAFLD的防治中发挥重要作用。本文对线粒体功能紊乱在MAFLD各病理过程中的作用及中医药的干预效应进行综述,以期从线粒体功能角度为中医药防治MAFLD提供新的思路与方法。Abstract: Metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a chronic liver disease closely associated with metabolic disorders, and the onset of MAFLD is associated with lipotoxicity caused by the accumulation of a large amount of fat in hepatocytes. Recent studies have shown that mitochondrial dysfunction is an important mechanism for the development of MAFLD, involving a series of pathological changes including mitochondrial oxidative stress, abnormal mitochondrial autophagy, abnormal mitochondrial apoptosis, and abnormal mitochondrial lipid metabolism. Based on the two characteristics of holistic view and syndrome differentiation-based treatment, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of MAFLD. This article reviews the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in various pathological processes of MAFLD and the intervention effect of TCM, in order to provide new ideas and methods for TCM in the prevention and treatment of MAFLD from the perspective of mitochondrial function.
-
[1] CHALASANI N, YOUNOSSI Z, LAVINE JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67( 1): 328- 357. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29367. [2] YOUNOSSI Z, TACKE F, ARRESE M, et al. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69( 6): 2672- 2682. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30251. [3] XIA WM, VEERAGANDHAM P, CAO Y, et al. Obesity causes mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in white adipocytes due to RalA activation[J]. Nat Metab, 2024, 6( 2): 273- 289. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-00978-0. [4] RAMANATHAN R, ALI AH, IBDAH JA. Mitochondrial dysfunction plays central role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 13): 7280. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23137280. [5] WANG XM, WANG YT, CHE Y, et al. Regulation of PGC-1α on mitochondrial function in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Med Res, 2023, 52( 9): 79- 84, 91. DOI: 10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2023.09.017.王雪梅, 王怡婷, 车悦, 等. PGC-1α调控非酒精性脂肪肝病线粒体功能的作用研究[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2023, 52( 9): 79- 84, 91. DOI: 10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2023.09.017. [6] BEAULANT A, DIA M, PILLOT B, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria miscommunication is an early and causal trigger of hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 3): 710- 722. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.03.017. [7] CHEN Z, TIAN RF, SHE ZG, et al. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 152: 116- 141. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.025. [8] PRASUN P. Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic syndrome[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2020, 1866( 10): 165838. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165838. [9] LEE KC, WU PS, LIN HC. Pathogenesis and treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and its fibrosis[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2023, 29( 1): 77- 98. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0237. [10] KANG HS, LIAO G, DEGRAFF LM, et al. CD44 plays a critical role in regulating diet-induced adipose inflammation, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8( 3): e58417. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058417. [11] WANG H, ZHANG W, ZUO L, et al. Intestinal dysbacteriosis contributes to decreased intestinal mucosal barrier function and increased bacterial translocation[J]. Lett Appl Microbiol, 2014, 58( 4): 384- 392. DOI: 10.1111/lam.12201. [12] MORIO B, PANTHU B, BASSOT A, et al. Role of mitochondria in liver metabolic health and diseases[J]. Cell Calcium, 2021, 94: 102336. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102336. [13] NEWMAN LE, SHADEL GS. Mitochondrial DNA release in innate immune signaling[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2023, 92: 299- 332. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-032620-104401. [14] MYINT M, OPPEDISANO F, de GIORGI V, et al. Inflammatory signaling in NASH driven by hepatocyte mitochondrial dysfunctions[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21( 1): 757. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04627-0. [15] PAIK S, KIM JK, SILWAL P, et al. An update on the regulatory mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18( 5): 1141- 1160. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-021-00670-3. [16] RITCHIE C, CAROZZA JA, LI LY. Biochemistry, cell biology, and pathophysiology of the innate immune cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2022, 91: 599- 628. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-040320-101629. [17] SHI HB, MENG S, QIU JH, et al. MoAti1 mediates mitophagy by facilitating recruitment of MoAtg8 to promote invasive growth in Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Mol Plant Pathol, 2024, 25( 3): e13439. DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13439. [18] GORDY C, HE YW. The crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis: Where does this lead[J]. Protein Cell, 2012, 3( 1): 17- 27. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-011-1127-x. [19] CHEN JH, ZHOU ZH. Effect of Qizhu prescription on a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease incluced by high-fat, highfructose, and high-cholesterol diet and its mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 11): 2205- 2212. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241113.陈佳豪, 周振华. 芪术方对高脂高果糖高胆固醇诱导的非酒精性脂肪性肝病小鼠模型的影响及其机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 11): 2205- 2212. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241113. [20] ZONG Y, LI H, LIAO P, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction: Mechanisms and advances in therapy[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9( 1): 124. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-024-01839-8. [21] MADRIGAL-MATUTE J, CUERVO AM. Regulation of liver metabolism by autophagy[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150( 2): 328- 339. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.042. [22] UNDAMATLA R, FAGUNLOYE OG, CHEN J, et al. Reduced mitophagy is an early feature of NAFLD and liver-specific PARKIN knockout hastens the onset of steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13: 7575. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-34710-x. [23] EDMUNDS LR, XIE BX, MILLS AM, et al. Liver-specific Prkn knockout mice are more susceptible to diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance[J]. Mol Metab, 2020, 41: 101051. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101051. [24] KAWAJIRI S, SAIKI S, SATO S, et al. PINK1 is recruited to mitochondria with parkin and associates with LC3 in mitophagy[J]. FEBS Lett, 2010, 584( 6): 1073- 1079. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.02.016. [25] MA XW, MCKEEN T, ZHANG JH, et al. Role and mechanisms of mitophagy in liver diseases[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 4): 837. DOI: 10.3390/cells9040837. [26] GAO SL, WEI LT, GUAN X, et al. Analysis of mitophagy-related genes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on bioinformatics and screening of traditional Chinese medicine for prevention and treatment[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2024, 55( 19): 6655- 6665. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2024.19.019.高松林, 韦柳婷, 管晓, 等. 基于生物信息学分析非酒精性脂肪性肝病的线粒体自噬相关基因及防治中药筛选[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55( 19): 6655- 6665. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2024.19.019. [27] PARK HS, SONG JW, PARK JH, et al. TXNIP/VDUP1 attenuates steatohepatitis via autophagy and fatty acid oxidation[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17( 9): 2549- 2564. DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1834711. [28] VILLANOVA L, CARECCIA S, de MARIA R, et al. Micro-economics of apoptosis in cancer: NcRNAs modulation of BCL-2 family members[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19( 4): 958. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19040958. [29] WANG YT, ZHENG XY, CHEN Y, et al. Palmitic acid increases apoptosis by mitochondrial pathway in hepatocytes with growth hormone deficiency[J]. J Third Mil Med Univ, 2021, 43( 21): 2366- 2374. DOI: 10.16016/j.1000-5404.202104150.王蕴婷, 郑晓雅, 陈月, 等. 生长激素受体敲低状态下棕榈酸通过线粒体途径加重肝细胞凋亡[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2021, 43( 21): 2366- 2374. DOI: 10.16016/j.1000-5404.202104150. [30] HUANG Y, DONG F, DU Q, et al. Swainsonine induces apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway and caspase activation in goat trophoblasts[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2014, 10( 7): 789- 797. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.9168. [31] LI XT, WANG SY, RUAN TY, et al. Transcriptomics-based analysis of the effect of compound Dancao granules on hepatocyte apoptosis in mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Acta Lab Animalis Sci Sin, 2024, 32( 12): 1543- 1555. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2024.12.005.李旭涛, 王四园, 阮天音, 等. 基于转录组学分析复方胆草颗粒对非酒精性脂肪性肝炎小鼠肝细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2024, 32( 12): 1543- 1555. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2024.12.005. [32] XIA AL, SUN BC. Research progress of macrophages in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases[J]. J Nanjing Med Univ Nat Sci, 2023, 43( 10): 1456- 1463. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20231020.夏安亮, 孙倍成. 巨噬细胞参与非酒精性脂肪性肝病的研究进展[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43( 10): 1456- 1463. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20231020. [33] ZHENG Y, QU H, XIONG X, et al. Deficiency of mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase contributes to hepatic steatosis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 1): 84- 97. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30507. [34] IPSEN DH, LYKKESFELDT J, TVEDEN-NYBORG P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2018, 75( 18): 3313- 3327. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-018-2860-6. [35] NASSIR F, IBDAH JA. Role of mitochondria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15( 5): 8713- 8742. DOI: 10.3390/ijms15058713. [36] REDDY JK, SAMBASIVA RAO M. Lipid Metabolism and Liver Inflammation. II. Fatty liver disease and fatty acid oxidation[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2006, 290( 5): g852- g858. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00521.2005. [37] LU WP, WEN ZF, LIU JY, et al. Improvement and mechanism of salvianolic acid B on non-alcoholic fatty liver in ApoE knockout mice[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2020, 36( 1): 31- 37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.01.008.卢万鹏, 温振帆, 刘家园, 等. 丹酚酸B对ApoE敲除小鼠非酒精性脂肪肝的改善运用及其机制研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2020, 36( 1): 31- 37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.01.008. [38] LI XW, SHI Z, ZHU YW, et al. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy in mice[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2020, 177( 15): 3591- 3607. DOI: 10.1111/bph.15083. [39] LIU PY, LIN HK, XU YY, et al. Frataxin-mediated PINK1-parkin-dependent mitophagy in hepatic steatosis: The protective effects of quercetin[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2018, 62( 16): e1800164. DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201800164. [40] WANG F, PARK JS, MA YQ, et al. Ginseng saponin enriched in Rh1 and Rg2 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting inflammasome activation[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13( 3): 856. DOI: 10.3390/nu13030856. [41] CHEN SW, YIN GL, SONG CY, et al. Diosgenin alleviates NAFLD induced by a high-fat diet in rats via mTOR/SREBP-1c/HSP60/MCAD/SCAD signaling pathway[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2023, 48( 19): 5304- 5314. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230601.705.陈素雯, 印国良, 宋超远, 等. 薯蓣皂苷元通过mTOR/SREBP-1c/HSP60/MCAD/SCAD信号通路缓解高脂饮食诱导的大鼠NAFLD[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48( 19): 5304- 5314. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230601.705. [42] ZHOU Y, WU RM, WANG XQ, et al. Activation of UQCRC2-dependent mitophagy by tetramethylpyrazine inhibits MLKL-mediated hepatocyte necroptosis in alcoholic liver disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 179: 301- 316. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.11.008. [43] ZHU XP, BIAN H, WANG L, et al. Berberine attenuates nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis through the AMPK-SREBP-1c-SCD1 pathway[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2019, 141: 192- 204. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.06.019. [44] DU XL, DI MALTA C, FANG ZY, et al. Nuciferine protects against high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance via activating TFEB-mediated autophagy-lysosomal pathway[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2022, 12( 6): 2869- 2886. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.12.012. [45] LIU JW, QIAO HJ, YANG JW. Impact of Lindera aggregata extract and endurance training on SIRT1-mediated mitochondrial function in NAFLD rats[J]. Mol Plant Breed, 2024, 22( 23): 7904- 7911. DOI: 10.13271/j.mpb.022.007904.刘精武, 乔虎军, 杨晶伟. 乌药醇提取物联合耐力训练对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠SIRT1介导的线粒体功能的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2024, 22( 23): 7904- 7911. DOI: 10.13271/j.mpb.022.007904. [46] HUANG RS, GUO F, LI YP, et al. Activation of AMPK by triptolide alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by improving hepatic lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 92: 153739. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153739. [47] XU JL, JIANG Y, HUANG XH, et al. Clinical observation on treating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with the Dachaihu decoction plus the Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction and lipid-lowering medicine[J]. Clin J Chin Med, 2022, 14( 5): 11- 15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2022.05.003.徐嘉兰, 江远, 黄小花, 等. 大柴胡汤合黄芪桂枝五物汤联合降脂药治疗非酒精性脂肪性肝炎的临床观察[J]. 中医临床研究, 2022, 14( 5): 11- 15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2022.05.003. [48] ZHANG X. Based on PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway, the mechanism of Jiawei Dachaihu Decoction in regulating mitochondrial autophagy and improving insulin resistance to obesity was studied[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of TCM, 2020.张旭. 基于PINK1/Parkin信号通路研究加味大柴胡汤调节线粒体自噬改善胰岛素抵抗肥胖的作用机制[D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2020. [49] ZHANG ZX, SHI JX, LIU FX, et al. Hujin prescription improves lipid metabolism in mice with metabolic associated fatty liver disease by regulating SIRT1/PGC1α signaling pathway[J]. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol, 2024, 35( 11): 1669- 1676. DOI: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2024.11.005.张梓煊, 施家希, 刘付轩, 等. 虎金方调节SIRT1/PGC1α信号通路改善代谢相关脂肪性肝病小鼠的脂质代谢研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2024, 35( 11): 1669- 1676. DOI: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2024.11.005. [50] LIAO JB, SONG Y, WANG S, et al. Jian’gan Xiaozhi decoction regulates PINK1/parkin pathway mediated mitochondrial autophagy to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Zhejiang Chin Med Univ, 2024, 48( 8): 905- 914. DOI: 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2024.08.002.廖加抱, 宋云, 王斯, 等. 健肝消脂方调控PINK1/Parkin通路介导的线粒体自噬治疗非酒精性脂肪肝[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报, 2024, 48( 8): 905- 914. DOI: 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2024.08.002. [51] PAN LL, XIANG HJ, LIU GR. Study on the mechanism of Lipijiangzhuo recipe in improving nonalcoholic fatty liver in mice by regulating HIF-1α/PPARγ/BNIP3 mitochondrial autophagy pathway[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2024, 35( 8): 1862- 1867. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2024.08.16.潘琳琳, 相宏杰, 刘桂荣. 理脾降浊方通过调控HIF-1α/PPARγ/BNIP3线粒体自噬途径改善小鼠非酒精性脂肪肝的机制研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2024, 35( 8): 1862- 1867. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2024.08.16. [52] SUN DQ, ZHOU XL, WU T, et al. Study on the mechanism of action of Lizhong Tang in ameliorating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating mitochondrial autophagy[J]. J Hainan Med Univ, 2023, 29( 21): 1614- 1619. DOI: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20231009.001.孙东琪, 周晓玲, 吴腾, 等. 理中汤通过调控线粒体自噬改善非酒精性脂肪性肝病的作用机制研究[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2023, 29( 21): 1614- 1619. DOI: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20231009.001. [53] XIAO YY, HAN X, CHEN QG, et al. Jianpi Qinghua Formula improves metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by modulating PGC1α/PPARα/CPT1A pathway[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2025, 50( 9): 2505- 2514. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250212.501.肖岩岩, 韩煦, 陈清光, 等. 健脾清化方调控PGC1α/PPARα/CPT1A通路改善代谢相关脂肪性肝病[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2025, 50( 9): 2505- 2514. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250212.501. -



 PDF下载 ( 796 KB)
PDF下载 ( 796 KB)

 下载:
下载:


