肝豆状核变性患者角膜K-F环分级与焦虑抑郁程度的相关性分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH251220
Association between corneal Kayser-Fleischer ring grading and the degree of anxiety-depression in patients with Wilson’s disease
-
摘要:
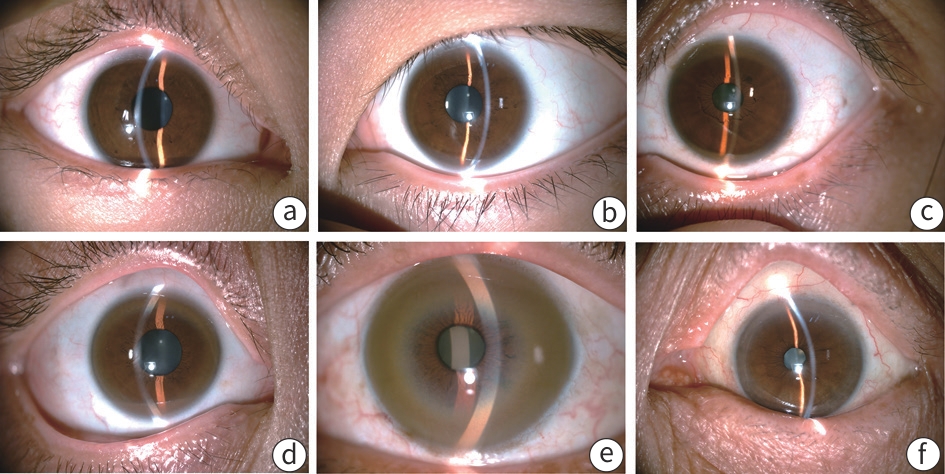
目的 探究角膜Kayser-Fleischer环(K-F环)不同分级对肝豆状核变性患者焦虑抑郁程度的影响。 方法 选取2012年8月—2020年2月安徽中医药大学第一附属医院眼科会诊的WD患者107例,在裂隙灯显微镜下进行角膜K-F环检查分级,分为0~4级。指导患者完成汉密尔顿焦虑量表(HAMA)和汉密尔顿抑郁量表(HAMD)测评,分析K-F环不同的分级与两个量表之间的差异及相关性。符合正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t或Dunnett’s T3检验。非正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验,进一步两两比较采用Bonferroni法。采用Spearman相关性分析将K-F环分级与HAMA、HAMD评分进行相关性分析。 结果 107例WD患者中K-F环最少的为0级5例(4.6%),最多的为4级44例(41.1%),另有1级18例(16.8%)、2级24例(22.4%)、3级16例(14.9%)。按照不同K-F环分级,HAMA评分、HAMD评分呈上升趋势(F值分别为16.340、12.760,P值均<0.001)。Spearman相关性分析发现K-F环分级与HAMA评分、HAMD评分呈正相关(r值分别为0.528 9、0.480 1,P值均<0.01)。 结论 角膜K-F环分级同HAMD、HAMA量表评分具有一定的相关性,可部分反映患者焦虑抑郁的程度。因此,临床医生应重视角膜K-F环的检查及其与临床症状的关系。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the impact of different grades of corneal Kayser-Fleischer (K-F) ring on the severity of anxiety and depression in patients with Wilson’s disease (WD). Methods A total of 107 patients with WD who received consultation in Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, from August 2012 to February 2020 were enrolled, and a slit-lamp microscope was used to determine the grade of corneal K-F ring (grades 0 — 4). The patients were instructed to complete Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) and Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD) assessments, and the correlation between K-F ring grade and the scores of the two scales was analyzed, as well as the differences in the scores of the two scales between the patients with different K-F ring grades. An analysis of variance was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test or the Dunnett’s T3 test was used for further comparison between two groups; the Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the Bonferroni method was used for further comparison between two groups. The Spearman correlation analysis was used to investigate the correlation between K-F ring grade and HAMA/HAMD score. Results Among the 107 patients with WD, the patients with grade 0 K-F ring accounted for the lowest proportion of 4.6% (5/107), while the patients with grade 4 K-F ring accounted for the highest proportion of 41.1% (44/107), and the patients with grade 1 K-F ring, grade 2 K-F ring, and grade 3 K-F ring accounted for 16.8% (18/107), 22.4% (24/107), and 14.9% (16/107), respectively. HAMA and HAMD scores tended to increase with the increase in K-F ring grade (F=16.340 and 12.760, both P <0.001). The Spearman correlation analysis showed that K-F ring grade was positively correlated with HAMA and HAMD scores (r=0.528 9 and 0.480 1, both P<0.01). Conclusion There is a certain correlation between corneal K-F ring grading and HAMD/HAMA scores, which can partially reflect the severity of anxiety and depression in patients. Therefore, clinicians should emphasize K-F ring examination and its association with clinical symptoms. -
表 1 各组患者一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general information of patients between different K-F ring grading groups
指标 0级(n=5) 1级(n=18) 2级(n=24) 3级(n=16) 4级(n=44) 统计值 P值 年龄(岁) 37.60±12.44 29.39±7.70 33.50±7.66 32.25±8.85 31.45±10.28 F=1.019 0.401 病程(月) 12.0(5.5~240.0) 54.0(21.0~87.0) 42.5(24.0~72.0) 78.0(15.0~135.0) 36.0(12.0~81.0) F=0.872 0.484 性别[例(%)] χ²=5.268 0.261 男 2(40.0) 15(83.3) 13(54.1) 10(62.5) 26(59.0) 女 3(60.0) 3(16.6) 11(45.8) 6(37.5) 18(41.0) 表 2 不同K-F环分级组间HAMA评分比较
Table 2. Comparison of HAMA scores between different K-F ring grading groups
组别 例数 HAMA评分(分) 0级 5 4.800±1.304 1级 18 8.444±4.792 2级 24 12.630±3.0191) 3级 16 17.560±3.5771)2)3) 4级 44 15.910±6.7301)2) F值 16.340 P值 <0.001 注:与0级比较,1)P<0.05;与1级比较,2)P<0.05;与2级比较,3)P<0.05。
表 3 不同K-F环分级组间HAMD评分比较
Table 3. Comparison of HAMD scores between different K-F ring grading groups
组别 例数 HAMD评分(分) 0级 5 2.00(0.00~2.50)1) 1级 18 3.00(1.75~6.00)1) 2级 24 5.00(2.00~8.00)1) 3级 16 5.50(2.25~17.75)1) 4级 44 13.00(2.00~22.00) F值 12.760 P值 <0.001 注:与4级比较,1)P<0.05。
-
[1] ROSENCRANTZ R, SCHILSKY M. Wilson disease: Pathogenesis and clinical considerations in diagnosis and treatment[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2011, 31( 3): 245- 259. DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1286056. [2] BANDMANN O, WEISS KH, KALER SG. Wilson’s disease and other neurological copper disorders[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2015, 14( 1): 103- 113. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70190-5. [3] LUCENA-VALERA A, RUZ-ZAFRA P, AMPUERO J. Wilson’s disease: Overview[J]. Med Clin(Barc), 2023, 160( 6): 261- 267. DOI: 10.1016/j.medcli.2022.12.016. [4] XIE JJ, WU ZY. Wilson’s disease in China[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2017, 33( 3): 323- 330. DOI: 10.1007/s12264-017-0107-4. [5] TELINIUS N, OTT P, SANDAHL T, et al. Scheimpflug imaging of the Danish cohort of patients with Wilson disease[J]. Cornea, 2019, 38( 8): 998- 1002. DOI: 10.1097/ico.0000000000001959. [6] ROBERTS EA, SCHILSKY ML. Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: An update[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 47( 6): 2089- 2111. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22261. [7] CHEN FF, HU FY, CAO XL, et al. Response to D-penicillamine treatment in patients with Wilson’s disease and different degree of Kayser-Fleischer ring[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2024, 27( 1): 145- 147. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2024.01.037.陈芬芬, 胡风云, 曹晓莉, 等. 肝豆状核变性患者角膜K-F环与临床病情程度关系探讨[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2024, 27( 1): 145- 147. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2024.01.037. [8] HAN XQ. Application of anxiety and depression in general hospital[J]. Chin Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 21( 11): 583- 584. DOI: 10.16066/j.1672-7002.2014.11.008.韩学青. 焦虑抑郁量表在综合医院的应用[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2014, 21( 11): 583- 584. DOI: 10.16066/j.1672-7002.2014.11.008. [9] AKIL M, BREWER GJ. Psychiatric and behavioral abnormalities in Wilson’s[J]. Adv Neurol, 1995, 65: 171- 178. [10] Inherited Metabolic Liver Disease Collaboration Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatolenticular degeneration(2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2022, 30( 1): 9- 20. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20211217-00603.中华医学会肝病学分会遗传代谢性肝病协作组. 肝豆状核变性诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2022, 30( 1): 9- 20. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20211217-00603. [11] QU J. Optical Theory and Methods[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2011: 40- 41.瞿佳. 眼视光学理论和方法[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011: 40- 41. [12] HU JY, ZHOU ZH, WANG X, et al. The effect of long-term copper removal therapy on the grading changes of K-F ring in the cornea of patients with hepatic steatosis[C]// The 18th National Neurology Academic Conference of the Chinese Medical Association. Chengdu, 2015: 703.胡纪源, 周志华, 王训, 等. 长期驱铜治疗对肝豆状核变性角膜K-F环分级变化的影响[C]// 中华医学会第十八次全国神经病学学术会议论文集. 成都, 2015: 703. [13] HAMILTON M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating[J]. Br J Med Psychol, 1959, 32( 1): 50- 55. DOI: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1959.tb00467.x. [14] HAMILTON M. A rating scale for depression[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 1960, 23( 1): 56- 62. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56. [15] XIA B. A case of hepatolenticular degeneration with ocular symptoms as the first symptom[J]. Chin J Ophthalmol Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 19( 5): 361- 362. DOI: 10.14166/j.issn.1671-2420.2019.05.018.夏冰. 以眼部症状首发的肝豆状核变性患者1例[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2019, 19( 5): 361- 362. DOI: 10.14166/j.issn.1671-2420.2019.05.018. [16] YANG YL, YANG WM, WANG H, et al. Correlation between muscle tension, clinical characteristics, and traditional Chinese medicine syndromes in patients with Wilson disease based on digital muscle function assessment system myoton PRO[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2025, 31( 15): 147- 154. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20241896.杨玉龙, 杨文明, 汪瀚, 等. 基于数字化肌肉功能评估系统 Myoton PRO探讨肝豆状核变性患者肌张力与临床特征及中医证型的相关性[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31( 15): 147- 154. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20241896. [17] ZHAO LQ, XU S, LIN H. Clinical characteristics and misdiagnosis analysis of 24 cases of mental disorders caused by hepatolenticular degeneration[J]. Aerosp Med, 2010, 21( 2): 167- 168. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1434.2010.02.019.赵立琼, 徐曙, 林汉. 24例肝豆状核变性所致精神障碍的临床特点与误诊分析[J]. 航空航天医药, 2010, 21( 2): 167- 168. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1434.2010.02.019. [18] ZHANG LY. Analysis of the results of self-rating anxiety and depression scale in 164 gastroscopy subjects[J]. Contemp Med, 2010, 16( 6): 44- 45. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2010.06.030.张兰英. 焦虑抑郁量表评定164例胃镜检查者的结果分析[J]. 当代医学, 2010, 16( 6): 44- 45. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2010.06.030. [19] WALTER G, LYNDON B. Depression in hepatolenticular degeneration(wikon’s disease)[J]. Aust N Z J Psychiatry, 1997, 31( 6): 880- 882. DOI: 10.3109/00048679709065517. [20] CAI YL, XU SH, YANG RM, et al. Anxiety and depression in patients with hepatolenticular degeneration[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2000, 8( 1): 46- 47. DOI: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2000.01.016.蔡永亮, 许圣弘, 杨任民, 等. 肝豆状核变性患者的焦虑、抑郁情绪调查[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2000, 8( 1): 46- 47. DOI: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2000.01.016. [21] FENU M, LIGGI M, DEMELIA E, et al. Kayser-Fleischer ring in Wilson’s disease: A cohort study[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2012, 23( 6): e150- e156. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2012.04.005. [22] XU LH. Correlation between Kayser-fleischer ring grades and clinical materials in 320 patients with hepatolenticular degeneration[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.徐柳慧. 320例肝豆状核变性患者角膜K-F环分级与临床相关性研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽中医药大学, 2020. [23] KANG LL, ZONG ZF, DONG K, et al. Effects of resveratrol on mental symptoms and corneal K-F ring in patients with Wilson’s disease[J]. Clin J Med Off, 2024, 52( 6): 627- 630. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2024.06.21.康丽利, 宗志峰, 董魁, 等. 白藜芦醇对肝豆状核变性患者精神症状、角膜K-F环影响[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2024, 52( 6): 627- 630. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2024.06.21. [24] PANCHERI P, PICARDI A, PASQUINI M, et al. Psychopathological dimensions of depression: A factor study of the 17-item Hamilton depression rating scale in unipolar depressed outpatients[J]. J Affect Disord, 2002, 68( 1): 41- 47. DOI: 10.1016/s0165-0327(00)00328-1. [25] HE W, YANG YL, YANG WM, et al. Correlation between Kayser-Fleischer ring grading and cognitive function in Wilson’s disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2025, 41( 6): 1150- 1155. DOI: 10.12449/JCH250622.何伟, 杨玉龙, 杨文明, 等. 肝豆状核变性K-F环分级与认知功能的相关性分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2025, 41( 6): 1150- 1155. DOI: 10.12449/JCH250622. -



 PDF下载 ( 901 KB)
PDF下载 ( 901 KB)

 下载:
下载:


