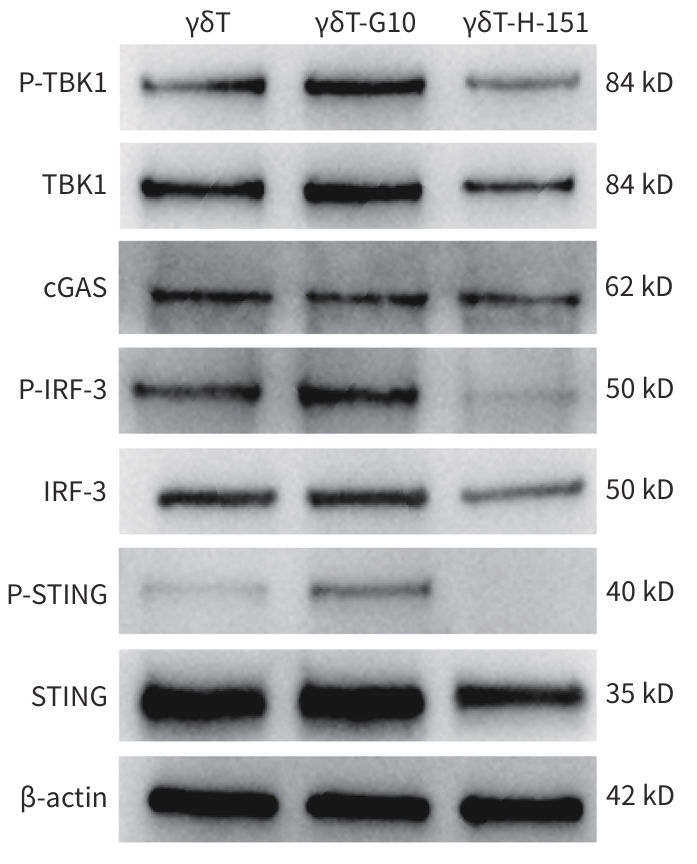
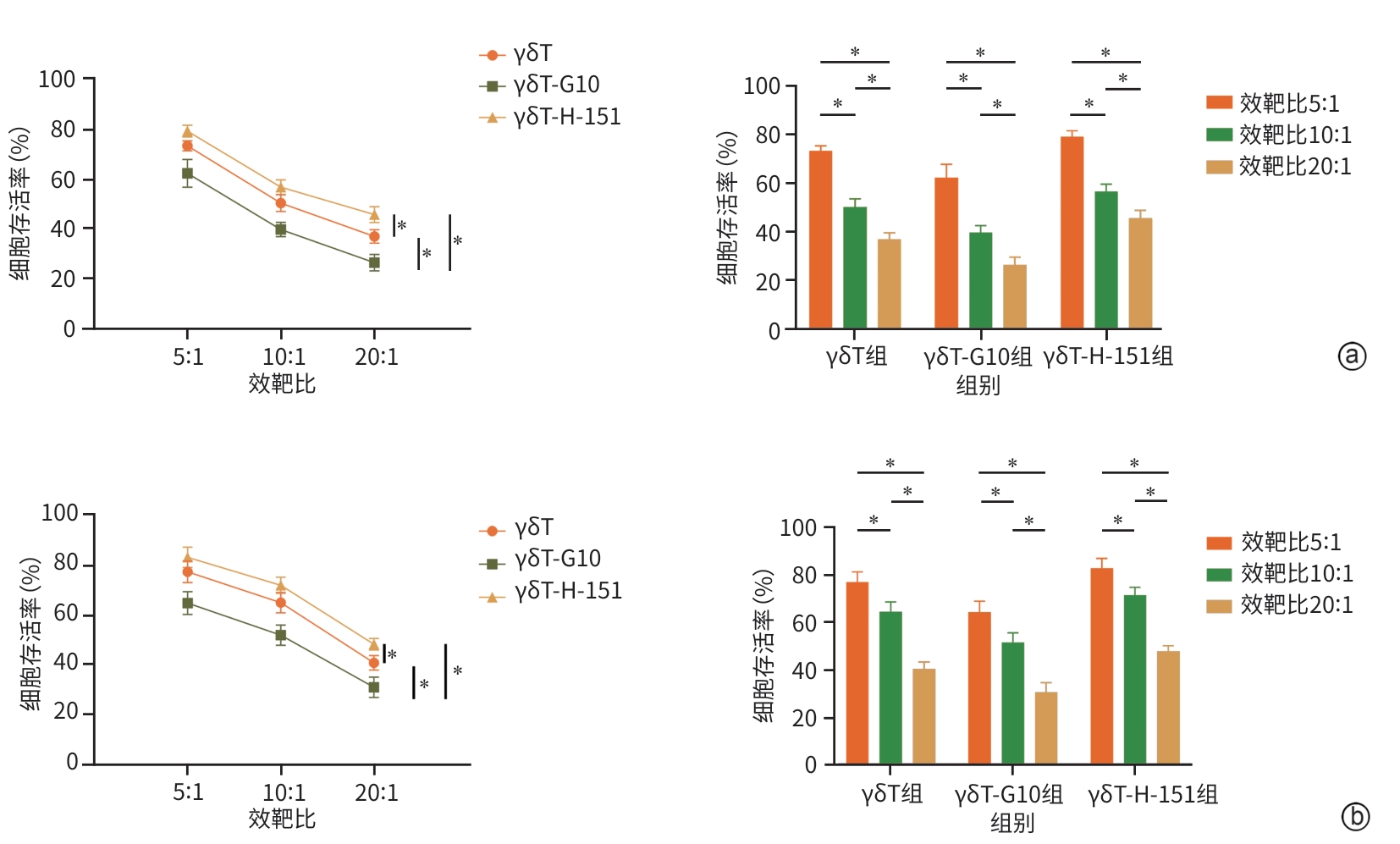
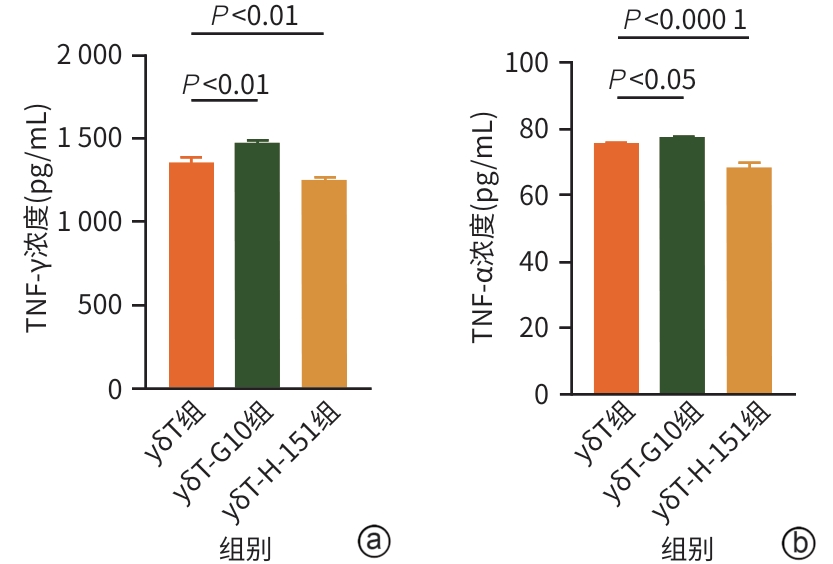
| [1] |
BRAY F, LAVERSANNE M, SUNG H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74( 3): 229- 263. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21834.
|
| [2] |
HAN BF, ZHENG RS, ZENG HM, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2024, 4( 1): 47- 53. DOI: 10.1016/j.jncc.2024.01.006.
|
| [3] |
DU BY, YU RH, GENG XQ, et al. The function of MSP-activated γδT cells in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 124( Pt A): 110893. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110893.
|
| [4] |
AMAJALA KC, GUDIVADA IP, MALLA RR. Gamma delta T cells: Role in immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Crit Rev Oncog, 2023, 28( 4): 41- 50. DOI: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2023049893.
|
| [5] |
XI XY, GUO Y, ZHU M, et al. Identification of new potential antigen recognized by γδT cells in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2021, 70( 7): 1917- 1927. DOI: 10.1007/s00262-020-02826-y.
|
| [6] |
BENMEBAREK MR, KARCHES CH, CADILHA BL, et al. Killing mechanisms of chimeric antigen receptor(CAR) T cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20( 6): 1283. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20061283.
|
| [7] |
OU L, ZHANG A, CHENG YX, et al. The cGAS-STING pathway: A promising immunotherapy target[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 795048. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.795048.
|
| [8] |
LI T, CHEN ZJ. The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway connects DNA damage to inflammation, senescence, and cancer[J]. J Exp Med, 2018, 215( 5): 1287- 1299. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20180139.
|
| [9] |
AN X, ZHU YY, ZHENG TS, et al. An analysis of the expression and association with immune cell infiltration of the cGAS/STING pathway in pan-cancer[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2019, 14: 80- 89. DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.11.003.
|
| [10] |
SUGAWARA Y, HIBI T. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biosci Trends, 2021, 15( 3): 138- 141. DOI: 10.5582/bst.2021.01094.
|
| [11] |
LIU DM, SONG TQ. Changes in and challenges regarding the surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in China[J]. Biosci Trends, 2021, 15( 3): 142- 147. DOI: 10.5582/bst.2021.01083.
|
| [12] |
LI R, JOHNSON R, YU GL, et al. Preservation of cell-based immunotherapies for clinical trials[J]. Cytotherapy, 2019, 21( 9): 943- 957. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.07.004.
|
| [13] |
ALNAGGAR M, XU Y, LI JX, et al. Allogenic Vγ9Vδ2 T cell as new potential immunotherapy drug for solid tumor: A case study for cholangiocarcinoma[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2019, 7( 1): 36. DOI: 10.1186/s40425-019-0501-8.
|
| [14] |
XU Y, XIANG Z, ALNAGGAR M, et al. Allogeneic Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell immunotherapy exhibits promising clinical safety and prolongs the survival of patients with late-stage lung or liver cancer[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18( 2): 427- 439. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-0515-7.
|
| [15] |
WANG XY, ZHANG HB, WANG YQ, et al. DNA sensing via the cGAS/STING pathway activates the immunoproteasome and adaptive T-cell immunity[J]. EMBO J, 2023, 42( 8): e110597. DOI: 10.15252/embj.2022110597.
|
| [16] |
MOTEDAYEN AVAL L, PEASE JE, SHARMA R, et al. Challenges and opportunities in the clinical development of STING agonists for cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9( 10): 3323. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9103323.
|
| [17] |
NAKAMURA T, SATO T, ENDO R, et al. STING agonist loaded lipid nanoparticles overcome anti-PD-1 resistance in melanoma lung metastasis via NK cell activation[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2021, 9( 7): e0028‑ 52. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002852.
|
| [18] |
KONDO M, IZUMI T, FUJIEDA N, et al. Expansion of human peripheral blood γδ T cells using zoledronate[J]. J Vis Exp, 2011( 55): 3182. DOI: 10.3791/3182.
|
| [19] |
HOERES T, SMETAK M, PRETSCHER D, et al. Improving the efficiency of Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell immunotherapy in cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 800. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00800.
|
| [20] |
DIELI F, VERMIJLEN D, FULFARO F, et al. Targeting human{gamma}delta}T cells with zoledronate and interleukin-2 for immunotherapy of hormone-refractory prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67( 15): 7450- 7457. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0199.
|
| [21] |
BANERJEE M, MIDDYA S, SHRIVASTAVA R, et al. G10 is a direct activator of human STING[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15( 9): e0237743. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237743.
|
| [22] |
HAAG SM, GULEN MF, REYMOND L, et al. Targeting STING with covalent small-molecule inhibitors[J]. Nature, 2018, 559( 7713): 269- 273. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0287-8.
|
| [23] |
ZHU ZX, LI HX, LU QZ, et al. mRNA-engineered CD5-CAR-γδTCD5- cells for the immunotherapy of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Adv Sci(Weinh), 2024, 11( 35): e2400024. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202400024.
|
| [24] |
BADOVINAC VP, TVINNEREIM AR, HARTY JT. Regulation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cell homeostasis by perforin and interferon-gamma[J]. Science, 2000, 290( 5495): 1354- 1358. DOI: 10.1126/science.290.5495.1354.
|
| [25] |
YIN KL, CHU KJ, LI M, et al. Immune regulatory networks and therapy of γδ T cells in liver cancer: Recent trends and advancements[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2024, 12( 3): 287- 297. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00355.
|
| [26] |
ZAKERI N, HALL A, SWADLING L, et al. Characterisation and induction of tissue-resident gamma delta T-cells to target hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13: 1372. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29012-1.
|
| [27] |
YUAN MG, WANG WJ, HAWES I, et al. Advancements in γδT cell engineering: Paving the way for enhanced cancer immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1360237. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1360237.
|
| [28] |
LI XM, LU HM, GU YZ, et al. Tim-3 suppresses the killing effect of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells on colon cancer cells by reducing perforin and granzyme B expression[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2020, 386( 1): 111719. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111719.
|
| [29] |
LIN JJ, ZENG DY, HE HY, et al. Gene therapy for human ovarian cancer cells using efficient expression of Fas gene combined with γδT cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16( 4): 3791- 3798. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7107.
|
| [30] |
AHN EY, PAN G, VICKERS SM, et al. IFN-gammaupregulates apoptosis-related molecules and enhances Fas-mediated apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Int J Cancer, 2002, 100( 4): 445- 451. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.10516.
|
| [31] |
ABE T, BARBER GN. Cytosolic-DNA-mediated, STING-dependent proinflammatory gene induction necessitates canonical NF-κB activation through TBK1[J]. J Virol, 2014, 88( 10): 5328- 5341. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00037-14.
|
| [32] |
VIEIRA RS, NASCIMENTO MS, NORONHA IH, et al. STING signaling drives production of innate cytokines, generation of CD8+ T cells and enhanced protection against Trypanosoma cruzi infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 12: 775346. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.775346.
|
| [33] |
KUSE N, SUN XM, AKAHOSHI T, et al. Priming of HIV-1-specific CD8+ T cells with strong functional properties from naïve T cells[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 42: 109- 119. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.078.
|
| [34] |
SU QY, WANG F, DONG ZB, et al. IFN-γ induces apoptosis in human melanocytes by activating the JAK1/STAT1 signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 22( 4): 3111- 3116. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11403.
|
| [35] |
BRAUMÜLLER H, WIEDER T, BRENNER E, et al. T-helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into senescence[J]. Nature, 2013, 494( 7437): 361- 365. DOI: 10.1038/nature11824.
|
| [36] |
BOIERI M, MARCHESE E, PHAM QM, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-stimulated CD4+ T cells induce senescence in advanced breast cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 1002692. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1002692.
|
| [37] |
JORGOVANOVIC D, SONG MJ, WANG LP, et al. Roles of IFN-γ in tumor progression and regression: A review[J]. Biomark Res, 2020, 8: 49. DOI: 10.1186/s40364-020-00228-x.
|
| [38] |
KAMMERTOENS T, FRIESE C, ARINA A, et al. Tumour ischaemia by interferon-γ resembles physiological blood vessel regression[J]. Nature, 2017, 545( 7652): 98- 102. DOI: 10.1038/nature22311.
|
| [39] |
KRUSE B, BUZZAI AC, SHRIDHAR N, et al. CD4+ T cell-induced inflammatory cell death controls immune-evasive tumours[J]. Nature, 2023, 618( 7967): 1033- 1040. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06199-x.
|
| [40] |
GUILLAUME J, PERZOLLI A, BOES M. Strategies to overcome low MHC-I expression in paediatric and adult tumours[J]. Immunother Adv, 2023, 4( 1): ltad028. DOI: 10.1093/immadv/ltad028.
|
| [41] |
CHOSA N, KYAKUMOTO S, KITO N, et al. Mechanism of Fas-mediated cell death and its enhancement by TNF-alpha in human salivary gland adenocarcinoma cell line HSG[J]. Eur J Oral Sci, 2004, 112( 4): 338- 346. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2004.00145.x.
|
| [42] |
BAKSHI HA, QUINN GA, NASEF MM, et al. Crocin inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis in colon cancer via TNF-α/NF-kB/VEGF pathways[J]. Cells, 2022, 11( 9): 1502. DOI: 10.3390/cells11091502.
|
| [43] |
DENG Y, GAO HY, WU QH. T-2 toxin induces immunosenescence in RAW264.7 macrophages by activating the HIF-1α/cGAS-STING pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72( 43): 24046- 24057. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c07268.
|
| [44] |
WU SY, XIAO Y, WEI JL, et al. MYC suppresses STING-dependent innate immunity by transcriptionally upregulating DNMT1 in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2021, 9( 7): e002528. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002528.
|
| [45] |
LIU FR, LIAO ZB, ZHANG ZG. MYC in liver cancer: Mechanisms and targeted therapy opportunities[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42( 45): 3303- 3318. DOI: 10.1038/s41388-023-02861-w.
|



 PDF下载 ( 105531 KB)
PDF下载 ( 105531 KB)

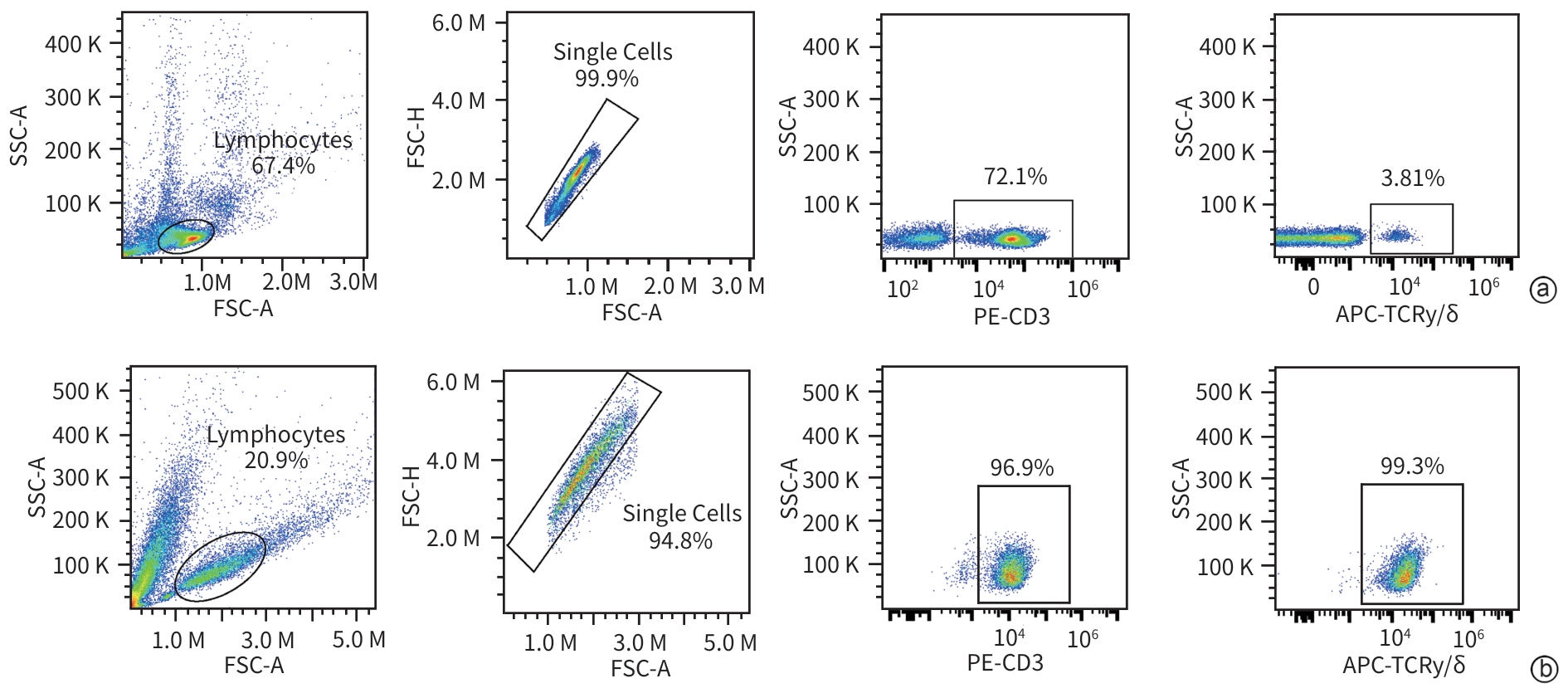
 下载:
下载: