cGAS-STING通路在肝脏疾病中的作用机制与治疗靶点研究进展
DOI: 10.12449/JCH251033
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:翟玉洁负责撰写论文;李向向负责修改论文;吴楚江、张亚南、贺昱昕、刘仲禹负责归纳文献;张久聪、梁斌负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Mechanism of action of the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes signaling pathway in liver diseases and research advances in therapeutic targets
-
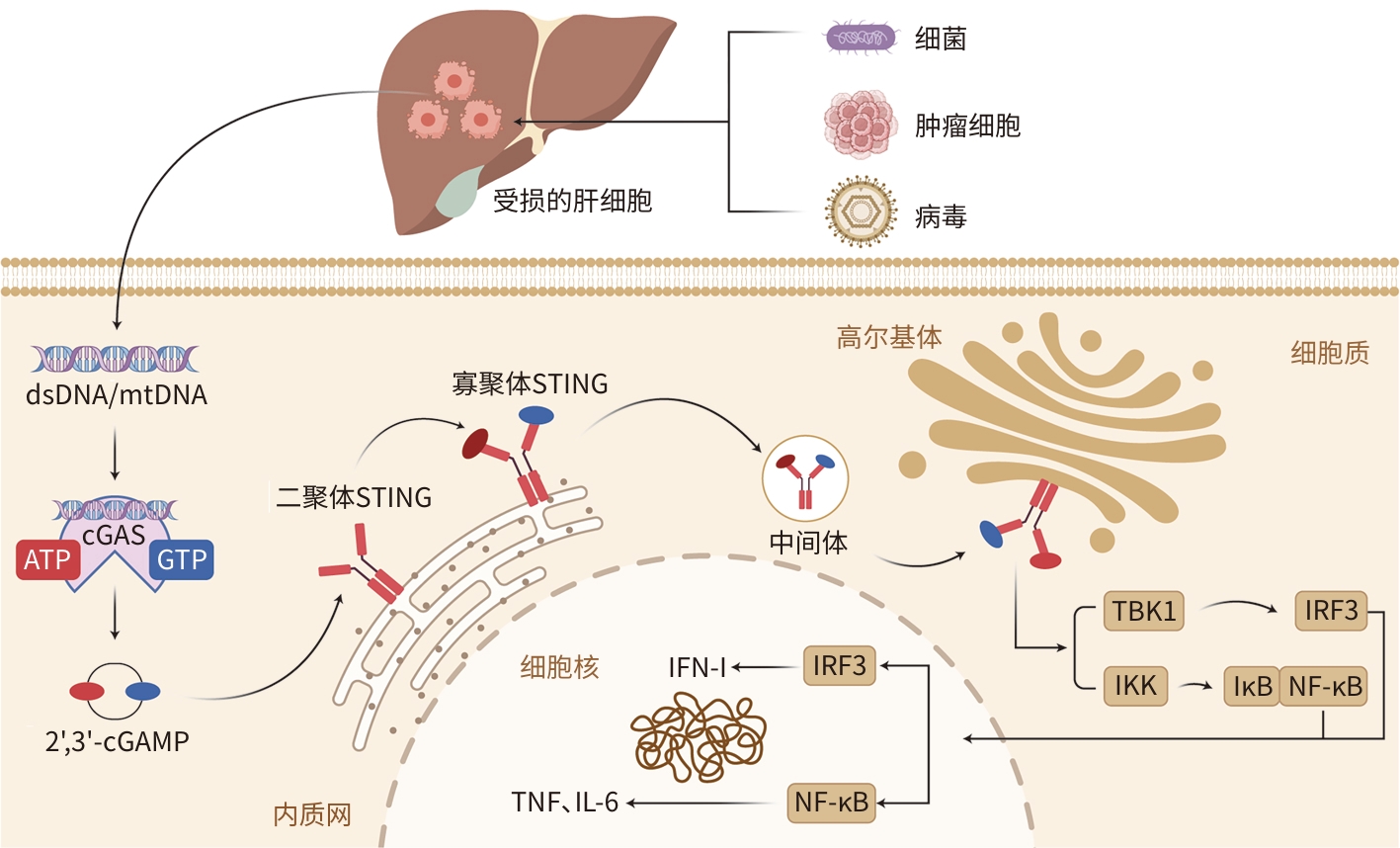
摘要: 肝脏疾病是一类由多种原因引发的复杂临床疾病,可导致肝细胞损伤及肝功能障碍,严重威胁人类健康。cGAS-STING信号通路在肝脏疾病的病程中发挥关键调控作用,参与病毒性肝炎、非酒精性脂肪性肝病、肝纤维化和肝癌等疾病的发生、发展与治疗。本文综述了cGAS-STING信号通路在炎症、自噬、抗病毒及氧化应激等过程中的调控机制,深入解析其在肝脏疾病中的分子作用,并探讨了其作为治疗肝脏疾病潜在靶点的应用前景,旨在为开发肝脏疾病的新型治疗策略提供理论依据。
-
关键词:
- 肝疾病 /
- cGAS-STING信号通路 /
- 病理过程 /
- 治疗学
Abstract: Liver diseases are a group of complex clinical conditions caused by various factors and can lead to hepatocyte damage and liver dysfunction, posing a serious threat to human health. The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling pathway plays a key regulatory role in the course of liver diseases and is involved in the development, progression, and treatment of various diseases such as viral hepatitis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, liver fibrosis, and liver cancer. This article reviews the regulatory mechanisms of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in processes such as inflammation, autophagy, antiviral response, and oxidative stress, analyzes its molecular function in liver diseases, and explores its application prospect as a potential target for the treatment of liver diseases, in order to provide a theoretical basis for developing novel therapeutic strategies for liver diseases.-
Key words:
- Liver Diseases /
- cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway /
- Pathologic Processes /
- Therapeutics
-
[1] DEVARBHAVI H, ASRANI SK, ARAB JP, et al. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 2): 516- 537. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017. [2] KIM J, KIM HS, CHUNG JH. Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial DNA release and activation of the cGAS-STING pathway[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2023, 55( 3): 510- 519. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-023-00965-7. [3] LI L. Activation of cGAS-STING-IRF3 pathway by dsDNA damages endothelial cells in systemic lupus erythematosus[D]. Dali: Dali University, 2024.李力. 双链DNA激活cGAS-STING-IRF3通路损伤系统性红斑狼疮患者内皮细胞[D]. 大理: 大理大学, 2024. [4] HERTZOG J, REHWINKEL J. Regulation and inhibition of the DNA sensor cGAS[J]. EMBO Rep, 2020, 21( 12): e51345. DOI: 10.15252/embr.202051345. [5] WU YK, LI ST. Role of post-translational modifications of cGAS in innate immunity[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 21): 7842. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21217842. [6] CHEN YY, TIAN ZG. HBV-induced immune imbalance in the development of HCC[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2048. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02048. [7] ZHANG MY. The mechanism of activating STING signaling pathwayto induce anti-HBV immune response[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022.张明媛. 激活STING信号通路诱导抗乙肝病毒免疫应答的机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022. [8] HU MM, SHU HB. Innate immune response to cytoplasmic DNA: Mechanisms and diseases[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2020, 38: 79- 98. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-070119-115052. [9] LI YQ, HE MJ, WANG ZY, et al. STING signaling activation inhibits HBV replication and attenuates the severity of liver injury and HBV-induced fibrosis[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2022, 19( 1): 92- 107. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-021-00801-w. [10] ZONG QY, ZHANG H, LIU FT, et al. Activation of the cGAS-STING pathway by viral dsDNA leading to M1 polarization of macrophages mediates antiviral activity against hepatitis B virus[J]. Immunobiology, 2024, 229( 3): 152810. DOI: 10.1016/j.imbio.2024.152810. [11] PAN H, ZHOU LM, ZOU JB, et al. Arsenic trioxide induces innate immune response and inflammatory response in chicken liver via cGAS-STING/NF-κB pathway[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol, 2024, 286: 110017. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2024.110017. [12] PAN Y, YANG K, SUN BB. A pilot study on the mechanism of abnormal iron metabolism in the chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Jiujiang Univ(Nat Sci), 2023, 38( 2): 95- 98. DOI: 10.19717/j.cnki.jjun.2023.02.020.潘颖, 杨凯, 孙蓓蓓. 铁代谢异常在乙型肝炎病毒感染慢性化中作用机制的初步研究[J]. 九江学院学报(自然科学版), 2023, 38( 2): 95- 98. DOI: 10.19717/j.cnki.jjun.2023.02.020. [13] LI HL, HU L, WANG LW, et al. Iron activates cGAS-STING signaling and promotes hepatic inflammation[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70( 7): 2211- 2220. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06681. [14] CHEN H, JIANG LS, CHEN S, et al. HBx inhibits DNA sensing signaling pathway via ubiquitination and autophagy of cGAS[J]. Virol J, 2022, 19( 1): 55. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-022-01785-3. [15] DENG H. Mechanism study of hepatitis B virus evasion from innate immunity activated by cGAS-STING pathway[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2023.邓辉. 乙肝病毒逃逸先天免疫cGAS-STING通路的机制研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2023. [16] ZHAO LN, YUAN HF, WANG YF, et al. HBV confers innate immune evasion through triggering HAT1/acetylation of H4K5/H4K12/miR-181a-5p or KPNA2/cGAS-STING/IFN-I signaling[J]. J Med Virol, 2023, 95( 7): e28966. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.28966. [17] CHEN HT, HE GR, CHEN Y, et al. Hepatitis B virus might be sensed by STING-dependent DNA sensors and attenuates the response of STING-dependent DNA sensing pathway in humans with acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Viral Immunol, 2020, 33( 10): 642- 651. DOI: 10.1089/vim.2020.0096. [18] RIAZI K, AZHARI H, CHARETTE JH, et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7( 9): 851- 861. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. [19] YANG JQ, ZHAO WX, ZHOU C, et al. Risk factors for the development of advanced liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and establishment of a nomogram model[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 8): 1579- 1584. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240812.杨金秋, 赵文霞, 周铖, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病发生进展期肝纤维化的危险因素及列线图预测模型构建[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 8): 1579- 1584. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240812. [20] YU YS, LIU Y, AN WS, et al. STING-mediated inflammation in Kupffer cells contributes to progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129( 2): 546- 555. DOI: 10.1172/JCI121842. [21] XU DW, QU XY, YANG T, et al. The Foxo1-YAP-Notch1 axis reprograms STING-mediated innate immunity in NASH progression[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2024, 56( 8): 1843- 1855. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01280-5. [22] WANG XX, RAO HY, ZHAO JM, et al. STING expression in monocyte-derived macrophages is associated with the progression of liver inflammation and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Lab Invest, 2020, 100( 4): 542- 552. DOI: 10.1038/s41374-019-0342-6. [23] FAN HY, SHI BM, LI HJ, et al. Correlation analysis between serum selenoprotein P and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in elders with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Diabetes, 2019, 27( 4): 250- 253. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2019.04.003.樊华英, 施毕旻, 李慧娟, 等. 血清硒蛋白P与老年2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关性研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2019, 27( 4): 250- 253. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2019.04.003. [24] MIAO ZR, WANG W, MIAO ZY, et al. Role of Selenoprotein W in participating in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Redox Biol, 2024, 71: 103114. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103114. [25] DONNE R, SAROUL-AINAMA M, CORDIER P, et al. Replication stress triggered by nucleotide pool imbalance drives DNA damage and cGAS-STING pathway activation in NAFLD[J]. Dev Cell, 2022, 57( 14): 1728- 1741. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.06.003. [26] AKHMETOVA K, BALASOV M, CHESNOKOV I. Drosophila STING protein has a role in lipid metabolism[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e67358. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67358. [27] WANG CX, HUCIK B, SARR O, et al. Delta-6 desaturase(Fads2) deficiency alters triacylglycerol/fatty acid cycling in murine white adipose tissue[J]. J Lipid Res, 2023, 64( 6): 100376. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100376. [28] VILA IK, CHAMMA H, STEER A, et al. STING orchestrates the crosstalk between polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism and inflammatory responses[J]. Cell Metab, 2022, 34( 1): 125- 139. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.12.007. [29] HUANG XY. Macrophage SCAP promotes metabolic inflammation and lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating STING-NF-κB signaling pathway[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2022.黄鑫宇. 巨噬细胞SCAP通过激活STING-NF-κB信号通路促进代谢性炎症和瘦型非酒精性脂肪性肝病的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2022. [30] YU CH, DAVIDSON S, HARAPAS CR, et al. TDP-43 triggers mitochondrial DNA release via mPTP to activate cGAS/STING in ALS[J]. Cell, 2020, 183( 3): 636- 649. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.020. [31] SHAN SL, LIU ZD, WANG S, et al. Mitochondrial oxidative stress regulates LonP1-TDP-43 pathway and rises mitochondrial damage in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2023, 264: 115409. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115409. [32] YONG H, WANG S, SONG FY. Activation of cGAS/STING pathway upon TDP-43-mediated mitochondrial injury may be involved in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis[J]. Liver Int, 2021, 41( 8): 1969- 1971. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14895. [33] BALCE DR, WANG YT, MCALLASTER MR, et al. UFMylation inhibits the proinflammatory capacity of interferon-γ-activated macrophages[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118( 1): e2011763118. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2011763118. [34] WANG Q, BU QF, LIU M, et al. XBP1-mediated activation of the STING signalling pathway in macrophages contributes to liver fibrosis progression[J]. JHEP Rep, 2022, 4( 11): 100555. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100555. [35] LÓPEZ-PÉREZ W, SAI K, SAKAMACHI Y, et al. TAK1 inhibition elicits mitochondrial ROS to block intracellular bacterial colonization[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118( 25): e2023647118. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2023647118. [36] SU WT, GAO WC, ZHANG R, et al. TAK1 deficiency promotes liver injury and tumorigenesis via ferroptosis and macrophage cGAS-STING signalling[J]. JHEP Rep, 2023, 5( 5): 100695. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100695. [37] TIAN SY. The expression of cGAS/STING pathway in cancertissues and its correlation with immune cell infiltration[D]. Haikou: Hainan Medical College, 2019.田思宇. 癌组织中cGAS/STING通路的表达及其与免疫细胞浸润的相关性分析[D]. 海口: 海南医学院, 2019. [38] ZHENG JP. Up-regulation of LAG-3 expression by cGAMP and the anti-tumor effect incombination with LAG-3 antibody[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2023.郑健培. cGAMP上调LAG-3表达及与LAG-3抗体联用的抗肿瘤效果研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2023. [39] LI X, PAN YF, CHEN YB, et al. Arsenic trioxide augments immunogenic cell death and induces cGAS-STING-IFN pathway activation in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15( 4): 300. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06685-8. [40] LI R, LIU XP, LI X, et al. Experimental study of ATP induced immunogenic cell death in immune response to hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2022, 21( 21): 2241- 2244. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.21.001.李然, 刘秀平, 李新, 等. ATP诱导免疫原性细胞死亡在肝癌免疫应答中的实验研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21( 21): 2241- 2244. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.21.001. [41] LUO SB, LUO RK, LU HY, et al. Activation of cGAS-STING signaling pathway promotes liver fibrosis and hepatic sinusoidal microthrombosis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 125: 111132. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111132. [42] ZHAO J, XU G, HOU XR, et al. Schisandrin C enhances cGAS-STING pathway activation and inhibits HBV replication[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 311: 116427. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116427. [43] SHU D, CHENG L, YUAN KF, et al. RVX-208, an inducer of Apolipoprotein A-I, inhibits the particle production of hepatitis B virus through activation of cGAS-STING pathway[J]. Antivir Ther, 2023, 28( 6): 13596535231219639. DOI: 10.1177/13596535231219639. [44] SAAD M, IBRAHIM W, HASANIN AH, et al. Evaluating the therapeutic potential of genetically engineered probiotic Zbiotics(ZB183) for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH) management via modulation of the cGAS-STING pathway[J]. RSC Med Chem, 2024, 15( 11): 3817- 3836. DOI: 10.1039/d4md00477a. [45] CHEN L, XIA SW, WANG SQ, et al. Naringenin is a potential immunomodulator for inhibiting liver fibrosis by inhibiting the cGAS-STING pathway[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2023, 11( 1): 26- 37. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00120. [46] CHEN L, XIA SW, WANG FX, et al. m6A methylation-induced NR1D1 ablation disrupts the HSC circadian clock and promotes hepatic fibrosis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2023, 189: 106704. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106704. [47] ZHAO DL, GAO YY, SU Y, et al. Oroxylin A regulates cGAS DNA hypermethylation induced by methionine metabolism to promote HSC senescence[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2023, 187: 106590. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106590. [48] GU LH, ZHAO CX, WANG YX, et al. Senescence of hepatic stellate cells by specific delivery of manganese for limiting liver fibrosis[J]. Nano Lett, 2024, 24( 4): 1062- 1073. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c03689. [49] LI K, GONG YH, QIU DB, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen facilitates teniposide-induced cGAS-STING activation to enhance the antitumor efficacy of PD-1 antibody in HCC[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2022, 10( 8): e004006. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004006. [50] SHI YX, WU ZF, LIU SR, et al. Targeting PRMT3 impairs methylation and oligomerization of HSP60 to boost anti-tumor immunity by activating cGAS/STING signaling[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15( 1): 7930. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52170-3. [51] SHENG HL, HUANG Y, XIAO YZ, et al. ATR inhibitor AZD6738 enhances the antitumor activity of radiotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors by potentiating the tumor immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2020, 8( 1): e000340. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000340. [52] XU Y, SUN F, TIAN YY, et al. Enhanced NK cell activation via eEF2K-mediated potentiation of the cGAS-STING pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 129: 111628. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111628. -



 PDF下载 ( 2121 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2121 KB)

 下载:
下载:


