CA280型细胞因子吸附柱治疗慢加急性肝衰竭的效果及安全性探讨
DOI: 10.12449/JCH251020
Efficacy and safety of CA280 cytokine adsorption column in treatment of acute-on-chronic liver failure
-
摘要:
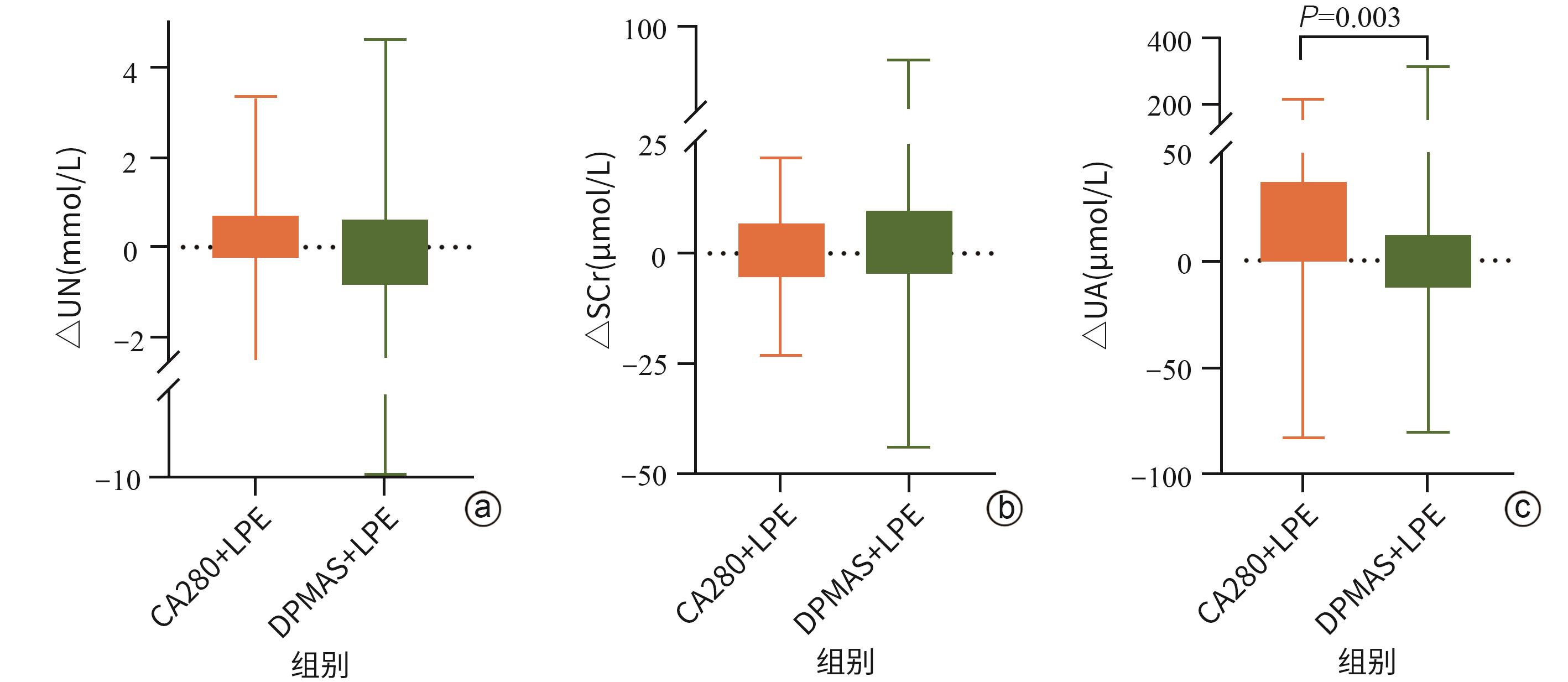
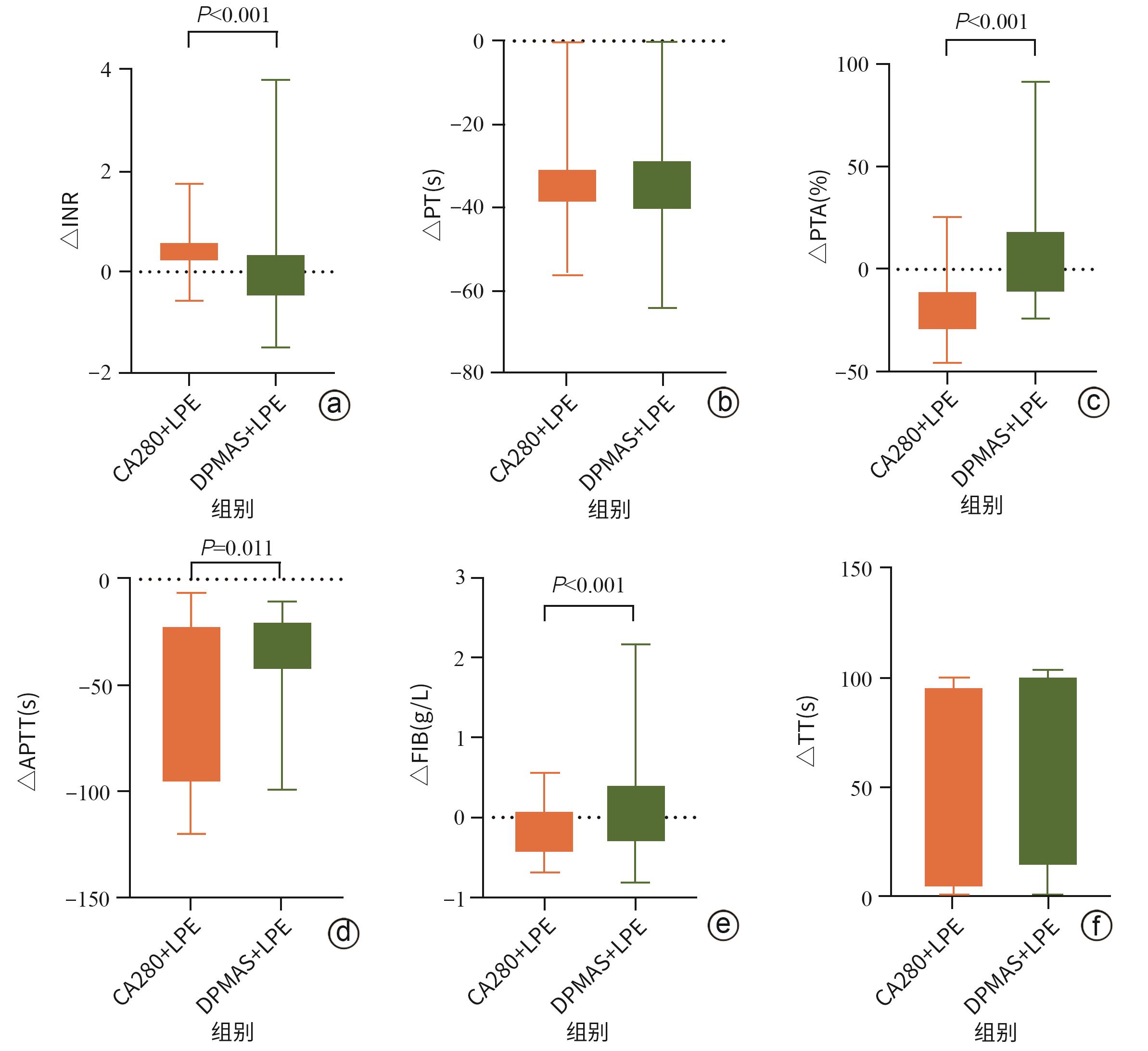
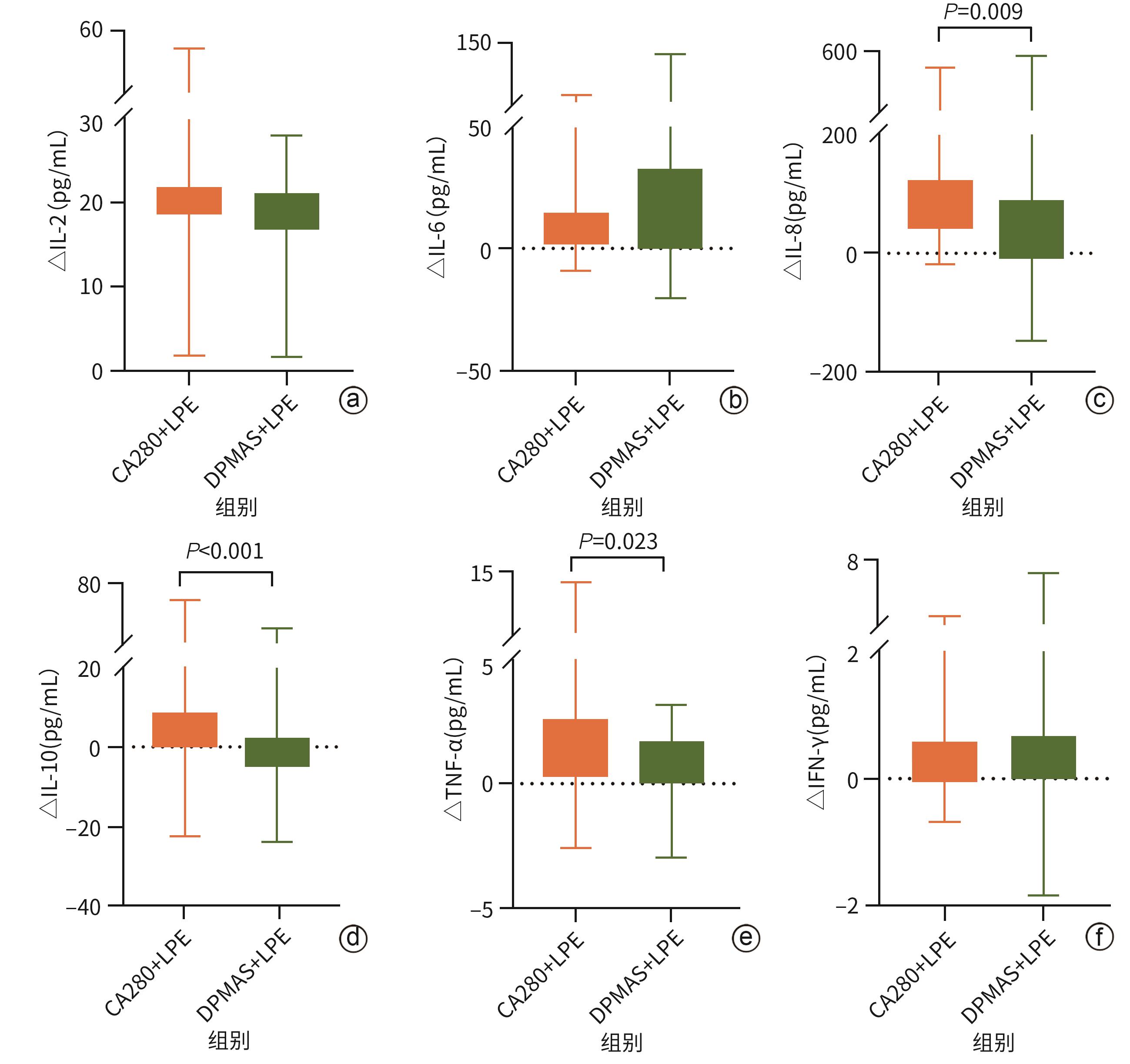
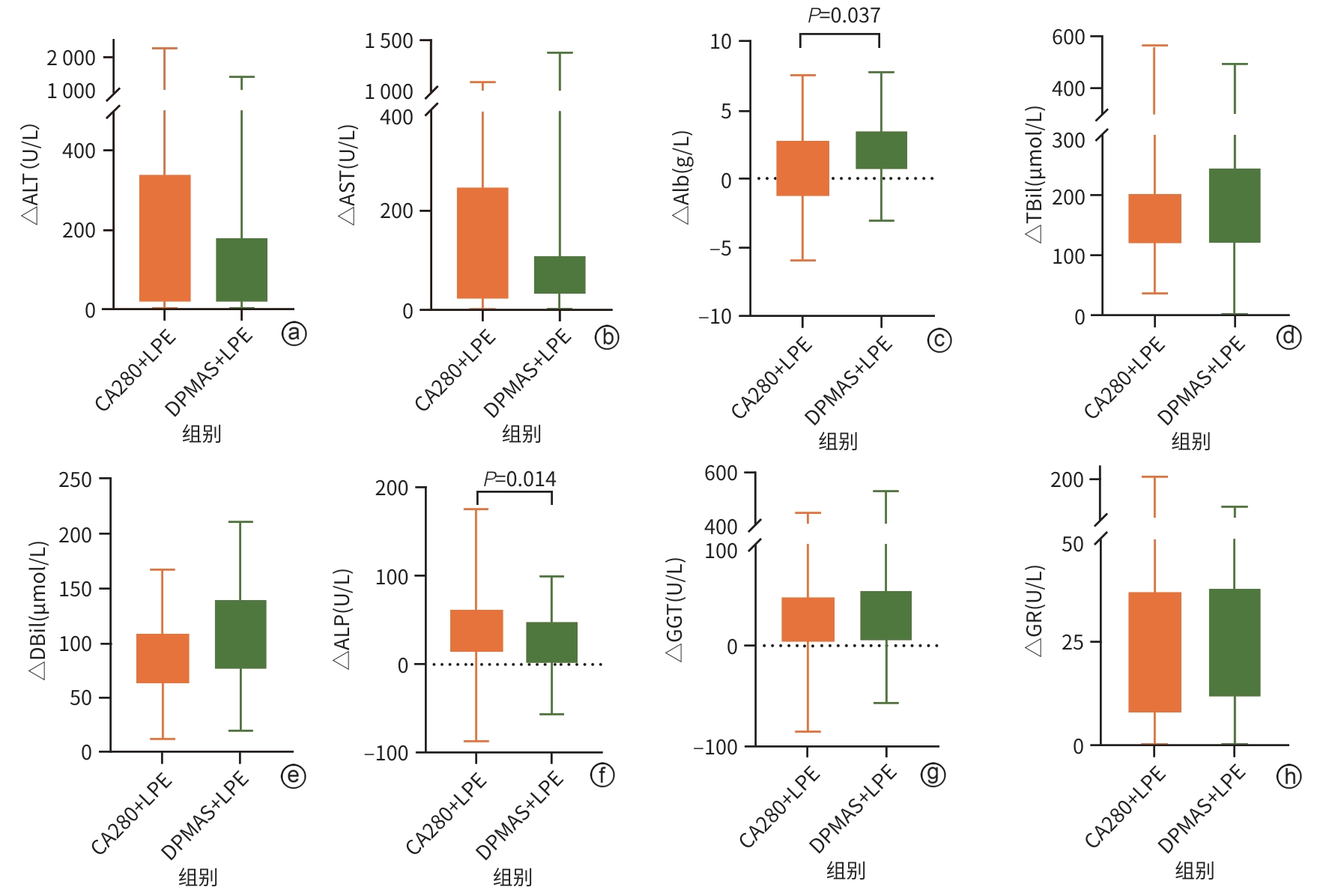
目的 探讨新型炎症因子吸附柱CA280联合低剂量血浆置换(LPE)治疗在慢加急性肝衰竭(ACLF)患者中的应用效果。 方法 采用前瞻性队列研究设计,纳入2023年6月—2025年1月南昌市第九医院收治的93例ACLF患者,随机分为DPMAS+LPE组(n=50)和CA280+LPE组(n=43)。两组均在内科综合治疗基础上分别接受DPMAS+LPE或CA280+LPE治疗。记录两组患者术前(基线)、术中(DPMAS或CA280)及术后(序贯LPE后)的血常规、肝功能指标、肾功能指标、电解质指标、凝血功能指标、细胞因子水平、不良事件及28 d预后情况。正态分布的计量资料组内治疗前后比较采用配对t检验,组间比较采用独立样本t检验;非正态分布的计量资料组内治疗前后比较采用Wilcoxon符号秩检验,组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验。计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确检验。相关性分析采用Spearman检验。 结果 CA280治疗后,ACLF患者的细胞因子如IL-6、IL-8、IL-10、TNF-α及IFN-γ水平,肝功能指标ALT、AST、ALP、TBil、DBil、Alb及谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR),肾功能指标尿素氮均较治疗前显著降低(P值均<0.05);凝血功能指标中凝血酶原时间(PT)、活化部分凝血活酶时间(APTT)、凝血酶时间(TT)和国际标准化比值(INR)较治疗前升高,凝血酶原活动度(PTA)和纤维蛋白原(FIB)降低,差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。CA280+LPE治疗相较于DPMAS+LPE对患者血清细胞因子IL-8(Z=-2.63,P=0.009)、IL-10(Z=-3.94,P<0.001)及TNF-α(Z=-1.53,P=0.023)的改善表现更优,两种人工肝支持系统治疗方案的肝功能改善效果(ALT、AST、GGT、GR、TBil、DBil)相似(P值均>0.05),但CA280+LPE对Alb(Z=-2.08,P=0.037)的消耗更为显著。CA280+LPE降低尿酸更为显著(Z=-2.97,P=0.003)。相较于DPMAS+LPE,CA280+LPE治疗后INR降低(Z=-4.01,P<0.001),APTT较前延长(Z=-2.53,P=0.011),PTA(Z=-6.28,P<0.001)及FIB(Z=-3.93,P<0.001)较治疗前升高更为显著。两组治疗过程中不良反应发生率和出院好转率差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。Spearman相关性分析显示,IL-6与WBC(r=0.22,P=0.042)、TBil(r=0.29,P=0.005)、FIB(r=-0.33,P=0.003)之间存在显著相关性;IL-8与APTT(r=0.37,P<0.001)、INR(r=0.25,P=0.013)呈正相关;TNF-α与WBC(r=0.40,P<0.001)和TBil(r=0.34,P<0.001)之间存在显著相关关系。 结论 相较于DPMAS,CA280联合LPE可有效清除ACLF患者促炎细胞因子并改善肝功能,但对Alb及凝血功能存在一定影响。该方案为ACLF个体化治疗提供了新的选择,可改善患者短期预后,但其长期疗效需进一步验证。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the application of the novel inflammatory factor adsorption column CA280 combined with low-dose plasma exchange (LPE) in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). Methods A prospective cohort study was designed, and a total of 93 ACLF patients who were admitted to The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang from June 2023 to January 2025 were enrolled and randomly divided into DPMAS+LPE group with 50 patients and CA280+LPE group with 43 patients. In addition to comprehensive medical treatment, the patients in the DPMAS+LPE group received DPMAS and LPE treatment, and those in the CA280+LPE group received CA280 and LPE treatment. The two groups were observed in terms of routine blood test results, liver function parameters, renal function markers, electrolytes, coagulation function parameters, cytokines, adverse events, and 28-day prognosis before surgery (baseline), during surgery (DPMAS or CA280), and after surgery (after sequential LPE treatment). The paired t-test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data before and after treatment within each group, and the independent-samples t test was used for comparison between groups; the Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data before and after treatment within each group, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison between groups. The chi-square test or the Fisher’s exact test was used for comparison of categorical data between groups, and the Spearman test was used for correlation analysis. Results After CA280 treatment, the ACLF patients had significant reductions in the levels of cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-α, and IFN-γ), liver function parameters (ALT, AST, ALP, TBil, DBil, Alb, and glutathione reductase), and the renal function marker urea nitrogen (all P<0.05), and in terms of coagulation function parameters, there were significant increases in prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time, and international normalized ratio (INR) and significant reductions in prothrombin activity (PTA) and fibrinogen (FIB) (all P<0.05). Compared with the DPMAS+LPE group, the CA280+LPE group showed better improvements in the serum cytokines IL-8 (Z=-2.63, P=0.009), IL-10 (Z=-3.94, P<0.001), and TNF-α (Z=-1.53, P=0.023), and the two artificial liver support systems had a similar effect in improving liver function (ALT, AST, GGT, GR, TBil, and DBil) (all P >0.05), but the CA280+LPE group showed a significantly greater reduction in Alb (Z=-2.08, P=0.037). CA280+LPE was more effective in reducing uric acid (Z=-2.97, P=0.003). Compared with DPMAS+LPE, CA280+LPE treatment resulted in a significant reduction in INR (Z=-4.01, P<0.001), a significant increase in APTT (Z=-2.53, P=0.011), and significant greater increases in PTA (Z=-6.28, P<0.001) and FIB (Z=-3.93, P<0.001). There were no significant differences in the incidence rates of adverse reactions and the rate of improvement at discharge between the two groups (all P>0.05). The Spearman correlation analysis showed that IL-6 was significantly correlated with WBC (r=0.22, P=0.042), TBil (r=0.29, P=0.005), and FIB (r=-0.33, P=0.003); IL-8 was positively correlated with APTT (r=0.37, P<0.001) and INR (r=0.25, P=0.013); TNF-α was significantly correlated with WBC (r=0.40, P<0.001) and TBil (r=0.34, P<0.001). Conclusion Compared with DPMAS, CA280 combined with LPE can effectively clear proinflammatory cytokines and improve liver function in ACLF patients, but it has a certain impact on Alb and coagulation function. This regimen provides a new option for the individualized treatment of ACLF and can improve the short-term prognosis of patients, but further studies are needed to verify its long-term efficacy. -
Key words:
- Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure /
- Liver, Artificial /
- Cytokine Adsorption
-
表 1 CA280治疗对ACLF患者肝功能的影响
Table 1. Effect of CA280 therapy on liver function in patients with ACLF
指标 CA280治疗前 CA280治疗后 统计值 P值 ALT(U/L) 168.80(64.80~630.40) 100.55(52.15~286.88) Z=-5.44 <0.001 AST(U/L) 135.15(72.08~427.22) 91.60(59.22~154.15) Z=-5.40 <0.001 Alb(g/L) 31.23±3.56 25.23±2.59 t=15.01 <0.001 TBil(μmol/L) 312.67±141.21 189.18±87.06 t=11.23 <0.001 DBil(μmol/L) 171.15±77.75 123.09±58.47 t=12.76 <0.001 ALP(U/L) 183.00(120.82~217.00) 156.00(122.00~187.75) Z=-2.99 0.003 GGT(U/L) 130.75(78.35~317.52) 106.15(64.75~296.43) Z=-2.74 0.006 GR(U/L) 90.35(73.60~115.67) 82.50(68.95~102.30) Z=-4.19 <0.001 表 2 CA280治疗对ACLF患者肾功能的影响
Table 2. Effect of CA280 therapy on renal function in patients with ACLF
指标 CA280治疗前 CA280治疗后 统计值 P值 UN(mmol/L) 3.75
(3.24~4.52)3.32
(2.51~4.15)Z=-2.59 0.010 SCr(μmol/L) 65.16±19.67 64.77±21.64 t=1.01 0.319 UA(μmol/L) 150.90±78.23 141.94±66.28 t=1.51 0.139 表 3 CA280治疗对ACLF患者凝血功能的影响
Table 3. Effect of CA280 therapy on coagulation function in patients with ACLF
指标 CA280治疗前 CA280治疗后 统计值 P值 INR 1.58
(1.44~1.85)2.34
(1.73~2.88)Z=-5.56 <0.001 PT(s) 20.20±5.84 26.80±9.27 t=-8.23 <0.001 PTA(%) 49.30±21.46 31.26±13.27 t=8.00 <0.001 APTT(s) 41.54±9.93 98.21±33.15 t=-7.54 <0.001 FIB(g/L) 1.60±0.54 1.54±0.45 t=1.31 <0.001 TT(s) 21.77±2.67 76.28±43.19 t=-5.25 <0.001 表 4 CA280治疗对ACLF患者血清细胞因子的影响
Table 4. Effect of CA280 therapy on cytokines in patients with ACLF
指标 CA280治疗前 CA280治疗后 统计值 P值 IL-2(pg/mL) 1.06(0.59~1.63) 1.18(0.52~2.29) Z=-0.79 0.431 IL-6(pg/mL) 20.24±14.25 11.16±5.56 t=4.21 <0.001 IL-8(pg/mL) 81.09(43.81~134.00) 50.22(26.88~79.41) Z=-3.79 <0.001 IL-10(pg/mL) 8.56(6.10~10.84) 6.61(4.79~10.53) Z=-2.14 0.033 TNF-α(pg/mL) 2.00(1.65~2.68) 1.35 (1.12~1.77) Z=-3.75 <0.001 IFN-γ(pg/mL) 0.53(0.31~0.85) 0.46(0.29~0.93) Z=-2.24 0.025 -
[1] BR VK, SARIN SK. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Terminology, mechanisms and management[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2023, 29( 3): 670- 689. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0103. [2] CASULLERAS M, ZHANG IW, LÓPEZ-VICARIO C, et al. Leukocytes, systemic inflammation and immunopathology in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 12): 2632. DOI: 10.3390/cells9122632. [3] HEO SK, YU HM, KIM DK, et al. LIGHT(TNFSF14) promotes the differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18( 8): e0289798. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289798. [4] ZHU BB, GAO FY, LI YX, et al. Serum cytokine and chemokine profiles and disease prognosis in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1133656. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1133656. [5] YE C, LI WY, LI L, et al. Glucocorticoid treatment strategies in liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 846091. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.846091. [6] QIANG R, LIU XZ, XU JC. The immune pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure and the danger hypothesis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 935160. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.935160. [7] FERNÁNDEZ J, ACEVEDO J, WIEST R, et al. Bacterial and fungal infections in acute-on-chronic liver failure: Prevalence, characteristics and impact on prognosis[J]. Gut, 2018, 67( 10): 1870- 1880. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314240. [8] MANTOVANI A, DINARELLO CA, MOLGORA M, et al. Interleukin-1 and related cytokines in the regulation of inflammation and immunity[J]. Immunity, 2019, 50( 4): 778- 795. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.012. [9] DU LY, MA YJ, ZHOU SQ, et al. A prognostic score for patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure treated with plasma exchange-centered artificial liver support system[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 1469. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81019-8. [10] ZHANG Z, ZHU J, DOU Y. Effect of artificial liver plasma exchange combined with CRRT in the treatment of hepatitis B-related chronic acute liver failure complicated with acute renal failure and its impact on prognosis[J]. Clin Misdiagn Misther, 2023, 36( 10): 86- 90. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2023.10.019.张泽, 朱健, 窦燕. 人工肝血浆置换联合CRRT治疗乙肝相关慢加急性肝衰竭合并急性肾衰竭效果及对预后的影响[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2023, 36( 10): 86- 90. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2023.10.019. [11] WU CC, PENG WT, CHENG D, et al. Efficacy and economic evaluation of nonbiological artificial liver therapy in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2023, 11( 2): 433- 440. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00106. [12] SHANG J, WANG MQ, WEN Q, et al. A novel prognostic model to predict outcome of artificial liver support system treatment[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 7510. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-87055-8. [13] HUANG YD, JU T, ZHANG HF, et al. Lower level of IL-28A as a predictive index of the artificial liver support system in effective treatment of patients with HBV-ACLF[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36( 12): e24766. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24766. [14] WANG L, XU WX, ZHU S, et al. Double plasma molecular adsorption system with sequential low-dose plasma exchange in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: A prospective study[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2023, 11( 4): 908- 917. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00254. [15] HE J, ZHANG XP, ZHOU X, et al. Application of double plasma molecular adsorption system in children with acute liver failure[J]. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2021, 23( 2): 180- 185. DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2010145.贺杰, 张新萍, 周雄, 等. 双重血浆分子吸附系统在儿童急性肝衰竭中的应用[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2021, 23( 2): 180- 185. DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2010145. [16] SEKANDARZAD A, WEBER E, PRAGER EP, et al. Cytokine adsorption in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure(CYTOHEP)-a single center, open-label, three-arm, randomized, controlled intervention trial[J]. Trials, 2022, 23( 1): 222. DOI: 10.1186/s13063-022-06139-6. [17] AGARWAL B, CAÑIZARES RB, SALIBA F, et al. Randomized, controlled clinical trial of the DIALIVE liver dialysis device versus standard of care in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 1): 79- 92. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.013. [18] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2024 version)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 12): 2371- 2387. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241206.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2024年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 12): 2371- 2387. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241206. [19] ZENG YY, GAN DK, ZHANG KG, et al. The impact of artificial liver support system on intestinal microbiota and serum bile acid profiles in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: A prospective cohort study[J]. Hepatol Int, 2024, 18( 5): 1540- 1554. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-024-10712-3. [20] BATEMAN RM, SHARPE MD, JAGGER JE, et al. 36th international symposium on intensive care and emergency medicine: Brussels, Belgium. 15-18 March 2016[J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20( Suppl 2): 94. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1208-6. [21] RONCO C, CHAWLA L, HUSAIN-SYED F, et al. Rationale for sequential extracorporeal therapy(SET) in sepsis[J]. Crit Care, 2023, 27( 1): 50. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-023-04310-2. [22] RADMANIC MATOTEK L, ZIDOVEC-LEPEJ S, SALEK N, et al. The impact of liver steatosis on interleukin and growth factors kinetics during chronic hepatitis C treatment[J]. J Clin Med, 2024, 13( 16): 4849. DOI: 10.3390/jcm13164849. [23] ZHOU C, ZHANG N, HE TT, et al. High levels of serum interleukin-6 increase mortality of hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26( 30): 4479- 4488. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i30.4479. [24] WU ZB, ZHENG YB, WANG K, et al. Plasma interleukin-6 level: A potential prognostic indicator of emergent HBV-associated ACLF[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 2021: 5545181. DOI: 10.1155/2021/5545181. [25] TARU V, SZABO G, MEHAL W, et al. Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: Hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation[J]. J Hepatol, 2024, 81( 5): 895- 910. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.06.016. [26] SCHWARZKOPF K, RÜSCHENBAUM S, BARAT S, et al. IL-22 and IL-22-binding protein are associated with development of and mortality from acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2019, 3( 3): 392- 405. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1303. [27] XIE ZB, DING L, LI YZ. Computed tomography image features under convolutional neural network algorithm in analysis of inflammatory factor level and prognosis of patients with hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Healthc Eng, 2021, 2021: 2110612. DOI: 10.1155/2021/2110612. [28] MOOKERJEE RP. Prognosis and biomarkers in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2016, 36( 2): 127- 132. DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1583200. -



 PDF下载 ( 55662 KB)
PDF下载 ( 55662 KB)

 下载:
下载: