血清HBV RNA对慢性乙型肝炎患者抗病毒治疗效果的评估价值
DOI: 10.12449/JCH251012
-
摘要:
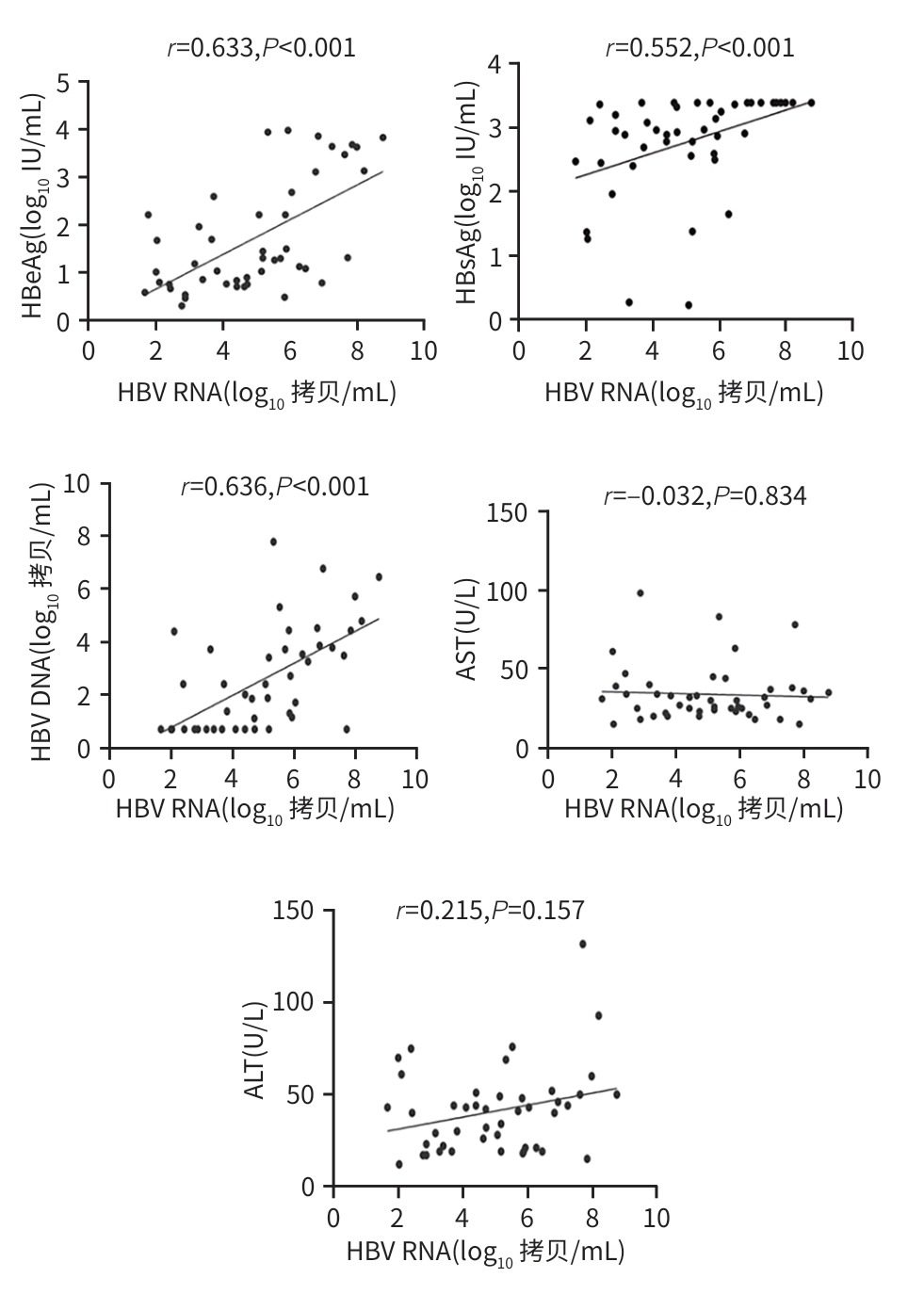
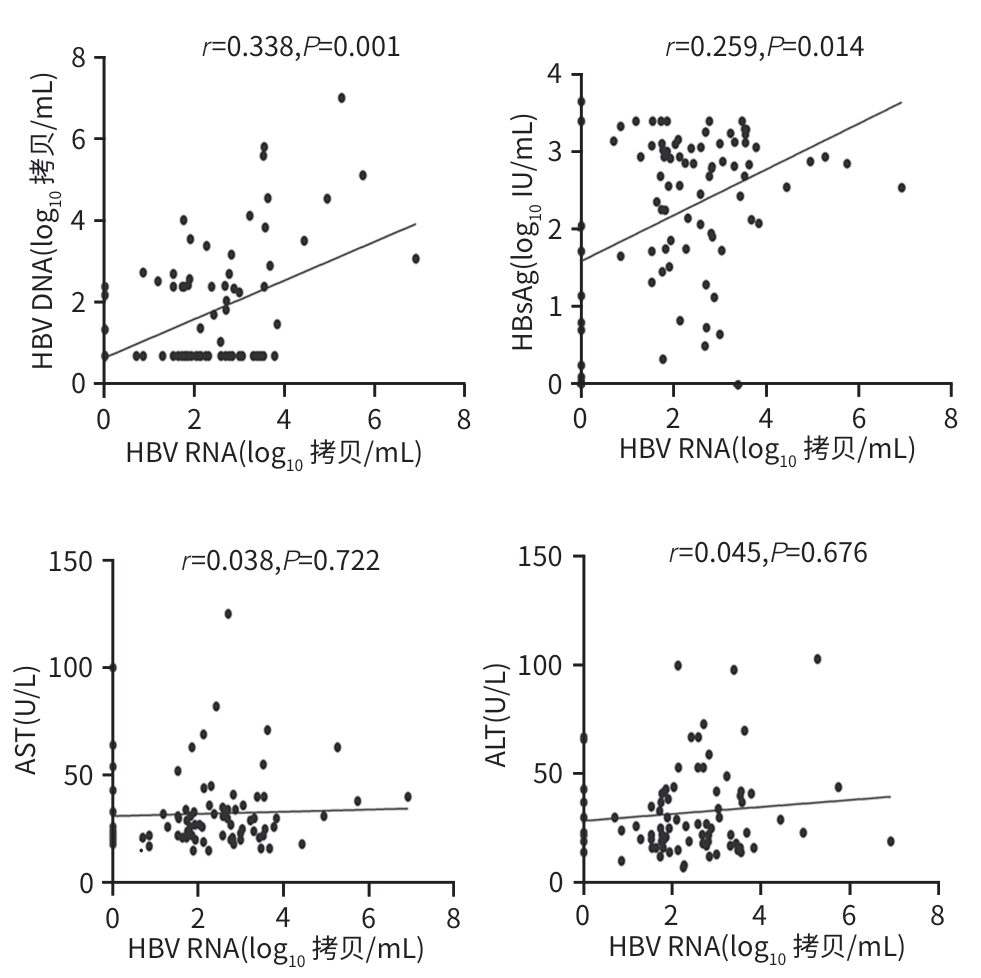
目的 探讨血清HBV RNA在评估慢性乙型肝炎患者抗病毒治疗中的作用,并探索其作为临床治疗中潜在生物标志物的可能性,以期为慢性乙型肝炎的临床治疗提供科学依据。 方法 纳入2023年4月—2024年5月于昆明医科大学第二附属医院诊断为慢性HBV感染者的134例患者为研究对象。完善HBV DNA、血清HBV RNA、肝功能、HBsAg、抗-HBs、HBeAg、抗-HBe、抗-HBc、肝脏瞬时弹性成像等检查。计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验或Mann-Whitney U检验;多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验或连续性修正χ2检验。相关性分析采用Pearson相关分析或Spearman相关分析。 结果 134慢性HBV感染者分为HBeAg阳性组(n=45)及HBeAg阴性组(n=89),两组间年龄、HBV DNA阳性率及定量值、血清HBV RNA阳性率及定量值、HBsAg、抗-HBe、ALT比较,差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。在HBeAg阴性组(n=89)的研究队列中,血清HBV RNA阴性(n=14)与阳性(n=75)患者间HBV DNA、HBsAg和GGT水平比较,差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。HBeAg阳性及阴性组使用抗病毒药物治疗时长≥1个月的患者分别有28例和62例,其中28例HBeAg阳性患者的HBV RNA阳性率达到了100%,62例HBeAg阴性患者的血清HBV RNA阳性率和定量水平在不同治疗时长组间比较,差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。89例HBeAg阴性组患者中经治疗62例,未治疗27例,两组HBV RNA水平分别为2.07(1.52~2.82)log10 拷贝/mL、2.69(1.80~3.55)log10 拷贝/mL,差异有统计学意义(Z=2.034,P=0.042)。HBeAg阴性组患者的血清HBV RNA仅与HBV DNA、HBsAg存在正相关(P值均<0.05);HBeAg阳性组患者的血清HBV RNA水平与HBV DNA、HBsAg及HBeAg均呈现显著正相关性(P值均<0.05)。 结论 抗病毒治疗可降低病毒载量,在高敏HBV DNA低于检测下限且HBeAg阴性的患者中,血清HBV RNA可填补检测病毒复制的“空白区”。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the role of serum HBV RNA in assessing antiviral therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B, as well as its potential as a biomarker in clinical therapy, and to provide a scientific basis for the clinical treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Methods A total of 134 patients who were diagnosed with chronic HBV infection in The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from April 2023 to May 2024 were enrolled as subjects, and related examinations were performed, including HBV DNA, serum HBV RNA, liver function, HBsAg, anti-HBs, HBeAg, anti-HBe, anti-HBc, and transient elastography of the liver. The independent-samples t test or the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison between multiple groups; the chi-square test or the continuity-adjusted chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. Pearson correlation analysis or Spearman correlation analysis was performed. Results The 134 patients with chronic HBV infection were divided into HBeAg-positive group with 45 patients and HBeAg-negative group with 89 patients, and there were significant differences between the two groups in age, the positive rate and quantitative value of HBV DNA, the positive rate and quantitative value of serum HBV RNA, HBsAg, anti-HBe, and ALT (all P<0.05). In the cohort study of the HBeAg negative group, there were significant differences in the levels of HBV DNA, HBsAg, and GGT between the serum HBV RNA-negative group with 14 patients and the serum HBV RNA-positive group with 75 patients (all P<0.05). There were 28 patients in the HBeAg-positive group and 62 in the HBeAg-positive group who used antiviral drugs for ≥1 month, and the 28 HBeAg-positive patients had an HBV RNA positive rate of 100%, while for the 62 HBeAg-negative patients, there were significant differences in the positive rate and level of serum HBV RNA between the patients with different durations of medication (both P<0.05). Among the 89 HBeAg-negative patients, there were 62 treatment-experienced patients and 27 treatment-naïve patients, and there was a significant difference between the two groups in HBV RNA level [2.07 (1.52 — 2.82) log10 copies/mL vs 2.69 (1.80 — 3.55) log10 copies/mL, Z=2.034, P=0.042]. For HBeAg-negative patients, serum HBV RNA was positively correlated with HBV DNA and HBsAg (both P<0.05), and for HBeAg-positive patients, serum HBV RNA was significantly positively correlated with HBV DNA, HBsAg, and HBeAg (all P<0.05). Conclusion Antiviral therapy can reduce viral load, and for HBeAg-negative patients with high-sensitivity HBV DNA below the lower limit of detection, serum HBV RNA can fill the “gap” in the detection of viral replication. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis B, Chronic /
- RNA, Viral /
- Therapeutics
-
表 1 HBeAg 阴性和阳性组的临床特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of clinical characteristics between HBeAg negative and positive groups
项目 HBeAg阴性组(n=89) HBeAg阳性组(n=45) 统计值 P值 性别[例(%)] χ2=0.89 0.346 男 56(62.92) 32(71.11) 女 33(37.08) 13(28.89) 年龄(岁) 41.81±10.57 35.09±9.86 t=3.55 <0.001 BMI(kg/m2) 22.20(20.70~24.31) 22.41(20.70~24.40) Z=-0.41 0.646 家族史[例(%)] 23(25.84) 11(24.44) χ2=0.03 0.861 HBV DNA阳性[例(%)] 39(43.82) 30(66.67) χ2=6.25 0.012 HBV RNA阳性[例(%)] 75(84.27) 45(100.00) χ2=6.31 0.012 HBV DNA(log10 拷贝/mL) 0.71(0.71~2.41) 2.01(0.71~3.82) Z=-2.77 0.006 HBV RNA(log10 拷贝/mL) 2.12(1.52~3.02) 5.14(3.33~6.36) Z=-7.07 <0.001 HBsAg(log10 IU/mL) 2.69(1.72~3.09) 2.97(2.53~3.41) Z=-3.13 0.002 抗-HBs(IU/mL) 0.19(0.16~0.31) 0.24(0.16~0.45) Z=-1.74 0.082 抗-HBe(IU/mL) 99.90(99.70~100.00) 51.30(0.00~60.40) Z=-8.09 <0.001 抗-HBc(IU/mL) 451.49(233.32~625.64) 435.42(230.27~575.79) Z=-0.73 0.462 Alb(g/L) 45.40(43.50~47.00) 44.30(42.70~46.20) Z=-1.56 0.118 ALT(U/L) 25.00(19.00~41.00) 41.00(21.00~50.00) Z=-2.59 0.010 AST(U/L) 26.00(21.25~34.00) 30.00(23.00~37.50) Z=-1.08 0.279 GGT(U/L) 21.50(14.00~37.00) 22.00(15.50~52.00) Z=-0.67 0.499 CHE(U/L) 9 319.50(7 815.30~10 614.50) 8 221.00(6 799.50~9 727.50) Z=-1.93 0.054 TBil(μmol/L) 15.00(10.90~18.92) 13.00(11.85~19.35) Z=-0.52 0.601 合并肝纤维化[例(%)] 45(50.56) 24(53.33) χ2=0.09 0.762 注:HBV DNA=0.71 log10 拷贝/mL提示低于检测下限。
表 2 HBeAg 阴性组中血清HBV RNA阳性率分析
Table 2. Analysis of serum HBV RNA positivity in HBeAg negative group
项目 HBV RNA阴性(n=14) HBV RNA阳性(n=75) 统计值 P值 性别[例(%)] χ2=0.52 0.473 男 10(71.4) 46(61.3) 女 4(28.6) 29(38.7) 年龄(岁) 42.00±11.16 41.77±10.54 t=0.07 0.942 HBV DNA(log10 拷贝/mL) 0.71(0.71~0.71) 0.71(0.71~2.58) Z=-2.18 0.029 HBsAg(log10 IU/mL) 0.48(0.24~1.80) 2.82(1.95~3.11) Z=-3.66 <0.001 抗-HBs(IU/mL) 0.29(0.15~0.75) 0.18(0.12~0.26) Z=-1.76 0.078 抗-HBe(IU/mL) 99.50(59.97~100.00) 99.90(98.00~100.00) Z=-1.21 0.225 抗-HBc(IU/mL) 312.94(151.09~537.40) 468.48(283.24~678.71) Z=-1.68 0.093 Alb(g/L) 44.60(43.55~48.38) 45.40(43.50~46.90) Z=-0.25 0.804 ALT(U/L) 26.50(21.25~43.00) 25.00(17.75~41.00) Z=-0.25 0.474 AST(U/L) 24.00(20.75~45.75) 26.50(21.75~34.00) Z=-0.13 0.897 GGT(U/L) 35.00(20.50~75.75) 20.50(13.00~32.00) Z=-2.20 0.028 注:HBV DNA=0.71 log10 拷贝/mL提示低于检测下限。
表 3 不同治疗时长血清HBV RNA水平
Table 3. Serum HBV RNA levels at different treatment durations
用药时长 例数 HBV RNA阳性率[例(%)] HBV RNA
(log10 拷贝/mL)
HBeAg阳性 28 1~12个月 21 21(100.0) 4.71(3.01~5.91) 13~24个月 4 4(100.0) 3.56(3.00~6.36) >24个月 3 3(100.0) 4.72(3.66~5.78) 统计值 H=0.242 P值 0.886 HBeAg阴性 62 1~12个月 28 25(89.3) 2.63(1.76~3.11) 13~24个月 15 13(86.7) 2.03(0.77~2.79) >24个月 19 12(63.2) 1.12(0.00~2.24) 统计值 χ2=5.991 H=9.212 P值 0.033 0.008 -
[1] GBD 2019 Hepatitis B Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of hepatitis B, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7( 9): 796- 829. DOI: 10.1016/s2468-1253(22)00124-8. [2] ZHANG SH, CUI FQ. Global progress, challenges and strategies in eliminating public threat of viral hepatitis[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2025, 14( 1): 9. DOI: 10.1186/s40249-025-01275-y. [3] WANG J, ZHANG S, ZHU C, et al. Treatment coverage of the 2024 updated WHO guidelines for patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Hepatol, 2025, 82( 6): e309- e310. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2025.01.039. [4] BURKI T. WHO’s 2024 global hepatitis report[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2024, 24( 6): e362- e363. DOI: 10.1016/s1473-3099(24)00307-4. [5] HAN GR, JIANG HX. New advances in antiviral therapy during pregnancy to block mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 11): 2158- 2163. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241105.韩国荣, 江红秀. 妊娠期抗病毒治疗阻断HBV母婴传播的新进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 11): 2158- 2163. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241105. [6] ZHUANG H. Progress towards elimination of hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 5): 857- 860. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240501.庄辉. 消除乙型肝炎进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 5): 857- 860. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240501. [7] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. Infect Dis Info, 2023, 36( 1): 1- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)[J]. 传染病信息, 2023, 36( 1): 1- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01. [8] GIERSCH K, ALLWEISS L, VOLZ T, et al. Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66( 2): 460- 462. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.028. [9] TANG LSY, COVERT E, WILSON E, et al. Chronic hepatitis B infection: A review[J]. JAMA, 2018, 319( 17): 1802- 1813. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.3795. [10] ZHANG SL, CAO MM, YANG F, et al. Analysis of the change trend of etiological burden of disease of liver cancer in the Chinese population from 1990 to 2019[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 1): 122- 130. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221112-00687.张绍丽, 曹毛毛, 杨帆, 等. 1990—2019年中国人群肝癌各病因疾病负担变化趋势分析[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22( 1): 122- 130. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221112-00687. [11] BOONSTRA A, SARI G. HBV cccDNA: The molecular reservoir of hepatitis B persistence and challenges to achieve viral eradication[J]. Biomolecules, 2025, 15( 1): 62. DOI: 10.3390/biom15010062. [12] YEH SH, LI CL, LIN YY, et al. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration drives carcinogenesis and provides a new biomarker for HBV-related HCC[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 15( 4): 921- 929. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.01.001. [13] DENG R, LIU S, SHEN S, et al. Circulating HBV RNA: From biology to clinical applications[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76( 5): 1520- 1530. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32479. [14] HE XJ, LONG YZ, ZHOU J, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA monitoring pegylated interferon therapy nucleos(t)ide analogues in the treatment of low viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis B curative effect[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 10): 1091- 1095. DOI: 10.16680/j.16713-826.2023.10.27.贺潇瑾, 龙云铸, 周娟, 等. 血清乙型肝炎病毒RNA监测聚乙二醇干扰素治疗核苷(酸)类似物经治低病毒载量慢性乙型肝炎患者疗效[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2023, 51( 10): 1091- 1095. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.10.27. [15] FARAG MS, van CAMPENHOUT MJH, PFEFFERKORN M, et al. Hepatitis B virus RNA as early predictor for response to pegylated interferon alpha in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 72( 2): 202- 211. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa013. [16] MAHAJAN A, KHARAWALA S, DESAI S, et al. Association of hepatitis B surface antigen levels with long-term complications in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic literature review[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2024, 31( 11): 746- 759. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13988. [17] ZHOU LL, DONG B, XIN JJ, et al. Liver histopathological features of HBeAg-negative patients in the indeterminate phase of low-viral-load chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2025, 41( 1): 52- 56. DOI: 10.12449/JCH250108.周路路, 东冰, 辛杰晶, 等. 低病毒载量HBeAg阴性不确定期慢性HBV感染者肝组织病理分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2025, 41( 1): 52- 56. DOI: 10.12449/JCH250108. [18] CAI G, GAO QE. Relationships between changes in serum HBV RNA levels and HBeAg positivity and cirrhosis in patients with CHB during antiviral therapy[J]. Shandong Med J, 2025, 65( 1): 104- 108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2025.01.022.蔡纲, 高庆娥. 慢性乙型肝炎患者抗病毒治疗中血清HBV RNA水平变化与HBeAg阳性及肝硬化的关系[J]. 山东医药, 2025, 65( 1): 104- 108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2025.01.022. [19] JIN MH, JIANG SW, HU AR, et al. Research progress on differential improvement and mechanism of nucleoside analogues or nucleotide analogues in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2025, 30( 6): 835- 848. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2025.06.014.金梦涵, 蒋素文, 胡爱荣, 等. 核苷与核苷酸类抗病毒药物对乙型肝炎相关肝细胞癌的差异性改善及其机制[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2025, 30( 6): 835- 848. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2025.06.014. [20] LI FH, QU LH, LIU YH, et al. PegIFN alpha-2a reduces relapse in HBeAg-negative patients after nucleo(s)tide analogue cessation: A randomized-controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2025, 82( 2): 211- 221. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.07.019. [21] JANSSEN HLA, SONNEVELD MJ. Combination therapy for chronic HBV infection[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 391( 22): 2163- 2168. DOI: 10.1056/nejme2410543. [22] WANG XM, CHI XM, WU RH, et al. Serum HBV RNA correlated with intrahepatic cccDNA more strongly than other HBV markers during peg-interferon treatment[J]. Virol J, 2021, 18( 1): 4. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-020-01471-2. [23] YE F, ZHAO WJ, YANG XL, et al. The decline of hbv RNA associated with HBeAg seroconversion and double-negative hbv DNA and RNA in chronic hepatitis b patients who received entecavir therapy: A 10-year retrospective cohort study[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10( 16): 897. DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-3265. [24] SONG GJ, YANG RF, JIN Q, et al. HBV pregenome RNA as a predictor of spontanous HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2023, 23( 1): 381. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-023-03023-8. [25] WOODDELL CI, YUEN MF, CHAN HL, et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9( 409): eaan0241. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aan0241. [26] MAK LY, CLOHERTY G, WONG DK, et al. HBV RNA profiles in patients with chronic hepatitis B under different disease phases and antiviral therapy[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 6): 2167- 2179. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31616. [27] WANG X, TANG XQ, HAN N, et al. Research progress of biomarkers of hepatitis B virus and clinical significance[J]. J Biomed Eng, 2023, 40( 6): 1242- 1248. DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.202309041.王馨, 唐小琼, 韩宁, 等. 乙型肝炎病毒生物标志物的研究进展及其临床意义[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2023, 40( 6): 1242- 1248. DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.202309041. -



 PDF下载 ( 24743 KB)
PDF下载 ( 24743 KB)

 下载:
下载: