核因子κB信号通路调控铁死亡的机制及在肝脏疾病中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250835
Mechanism of the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway regulating ferroptosis and its role in liver diseases
-
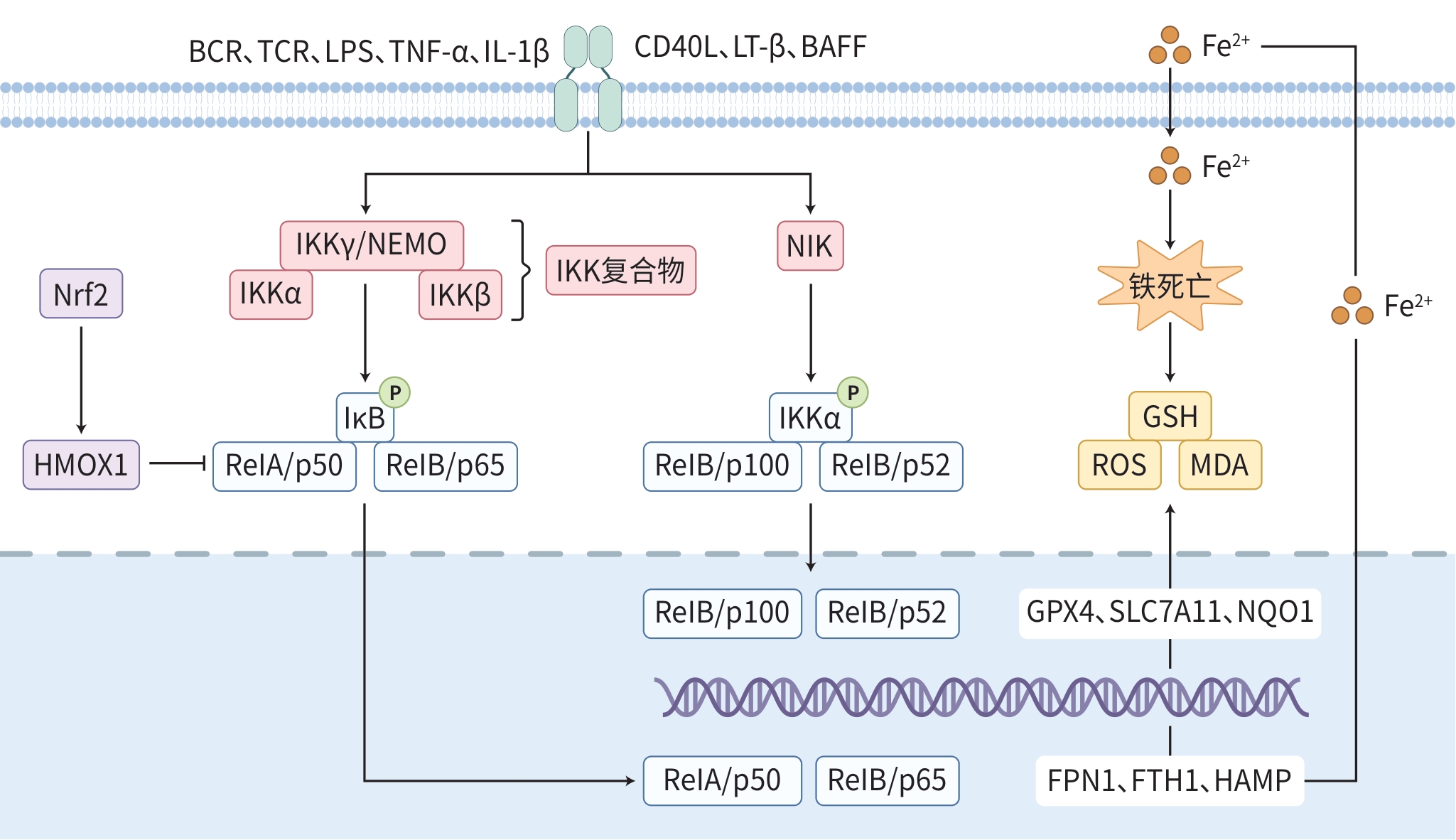
摘要: 核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路作为一种经典的炎症反应通路,在多种生理和病理过程中发挥着关键作用。铁死亡是一种新的非凋亡性细胞死亡形式,研究发现NF-κB信号通路与铁死亡之间存在紧密联系,影响着肝脏系统疾病的发生发展过程。因此,靶向NF-κB信号通路调节铁死亡在肝脏系统疾病的治疗中有巨大潜力。本文探讨了NF-κB信号通路对铁死亡过程中脂质代谢、铁离子代谢等关键环节的影响,以及正向或负向调控铁死亡的作用机制。同时,探讨了该信号通路调控铁死亡在肝损伤、非酒精性脂肪性肝病、酒精性肝病和肝细胞癌等肝脏系统疾病中的研究进展,为进一步理解肝脏疾病的发病机制以及开发新的治疗策略提供参考。Abstract: As a classical inflammatory response pathway, the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway plays a critical role in various physiological and pathological processes. Ferroptosis is a new form of non-apoptotic cell death, and recent studies have shown that there is a strong link between the NF-κB signaling pathway and ferroptosis, which affects the development and progression of liver diseases. Therefore, regulation of ferroptosis by targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway has a great potential in the treatment of liver diseases. This article discusses the influence of the NF-κB signaling pathway on the critical links such as lipid metabolism and iron metabolism during ferroptosis, as well as its mechanism of action in the positive and negative regulation of ferroptosis. Meanwhile, this article reviews the research advances in the role of this signaling pathway in liver diseases such as liver injury, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, alcoholic liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma through the regulation of ferroptosis, so as to provide a reference for further understanding of the pathogenesis of liver diseases and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
-
Key words:
- Nuclear Factor-κB /
- Ferroptosis /
- Liver Diseases
-
表 1 肝疾病中基于NF-κB信号通路的铁死亡调控分子及调控机制
Table 1. Regulatory molecules and mechanisms of ferroptosis based on NF-κB signalling pathway in liver diseases
疾病类型 第一作者
及年份药物靶点 作用机制 NF-κB
表达作用影响 作用结果 肝损伤 Chen[43]2022 组蛋白H3 NOD2/IκBα/
NF-κB p65激活 Fe2+、ROS↑
GPX4、GSH↓诱导急性肝衰竭肝巨噬细胞铁死亡 肝损伤 Zhong[44]2021 NF-κB诱导
激酶NIKNIK/IKKα/ROS 激活 ROS↑ 促进肝细胞铁死亡,加重肝损伤 肝损伤 Tak[46]2024 NEMO NEMO/Gα12/
GPX4抑制 GPX4↑ 保护肝细胞免受内质网应激诱导的
铁死亡肝损伤 Lin[47]2023 Caspase 6 NEMO/RIPK1/
IκBα激活 ASCL4↑GPX4↓ 促进肝细胞铁死亡 MAFLD Yao[50]2024 牙龈卟啉单
胞菌NF-κB/GPX4/
SLC7A11激活 GPX4、SLC7A11↓ 诱导MAFLD细胞铁死亡 MAFLD Yu[51]2021 EWCD Nrf2/NF-κB/ROS 抑制 ROS↓ 抑制MAFLD细胞铁死亡 MAFLD Yuan[52]2023 HMOX1 NF-κB/SLC7A11/
GPX4抑制 SLC7A11、GPX4↑ 抑制铁死亡,缓解非酒精性脂肪性
肝炎ALD Zmijewski[55]
2014酒精 HAMP mRNA/
NF-κB/Fe2+激活 Fe2+↑ 促进酒精性肝病细胞铁死亡 HCC Yao[57]2021 LIFR LIFR/NF-κB/
LCN2激活 Fe2+↓ 减弱HCC对铁死亡的敏感性 HCC Sun[58]2024 Bay11-7082 NF-κB/GPX4/
ROS抑制 ROS、MDA、Fe2+↑ 促进HepG2细胞铁死亡 HCC Wang[59]2023 阿司匹林 NF-κB/SLC7A11 抑制 SLC7A11↓ 促进HCC细胞铁死亡 HCC Lin[60]2023 白术内酯Ⅱ TRAF6/NF-κB/
ROS抑制 ROS、MDA↑,GSH、
SLC7A11、GPX4↓促进HCC细胞铁死亡 HCC Li[61]2024 DDX5 Wnt/β-catenin/
NIK/p52/RelB激活 Nrf2↑ 抑制索拉非尼诱导的HCC细胞铁
死亡注:Gα12,G蛋白亚基α12;Bay11-7082,NF-κB抑制剂;↑,上升或激活;↓,下降或抑制。
-
[1] JIANG XJ, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22( 4): 266- 282. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8. [2] LAWRENCE T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2009, 1( 6): a001651. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001651. [3] LUEDDE T, SCHWABE RF. NF-κB in the liver: Linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 8( 2): 108- 118. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.213. [4] ZHANG Q, LENARDO MJ, BALTIMORE D. 30 years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology[J]. Cell, 2017, 168( 1-2): 37- 57. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.012. [5] KAILEH M, SEN R. NF-κB function in B lymphocytes[J]. Immunol Rev, 2012, 246( 1): 254- 271. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01106.x. [6] KARIN M, BEN-NERIAH Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-[kappa] B activity[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2000, 18: 621- 663. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. [7] GAMBHIR S, VYAS D, HOLLIS M, et al. Nuclear factor kappa B role in inflammation associated gastrointestinal malignancies[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21( 11): 3174- 3183. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3174. [8] ISRAËL A. The IKK complex, a central regulator of NF-kappaB activation[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2010, 2( 3): a000158. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000158. [9] SUN SC. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Cell Res, 2011, 21( 1): 71- 85. DOI: 10.1038/cr.2010.177. [10] YAN HF, ZOU T, TUO QZ, et al. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms and links with diseases[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6( 1): 49. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-00428-9. [11] LIU MR, ZHU WT, PEI DS. System Xc-: A key regulatory target of ferroptosis in cancer[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2021, 39( 4): 1123- 1131. DOI: 10.1007/s10637-021-01070-0. [12] LIU J, KANG R, TANG DL. Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis[J]. FEBS J, 2022, 289( 22): 7038- 7050. DOI: 10.1111/febs.16059. [13] CHEN Y, FANG ZM, YI X, et al. The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14( 3): 205. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-05716-0. [14] LIANG DG, MINIKES AM, JIANG XJ. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling[J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82( 12): 2215- 2227. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.022. [15] YAN N, XU ZP, QU CH, et al. Dimethyl fumarate improves cognitive deficits in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis via NRF2/ARE/NF-κB signal pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 98: 107844. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107844. [16] CHEN DD, GENG Y, DENG ZW, et al. Inhibition of TLR4 alleviates heat stroke-induced cardiomyocyte injury by down-regulating inflammation and ferroptosis[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28( 5): 2297. DOI: 10.3390/molecules28052297. [17] MIN YQ, LI S, LIU XH, et al. Research advances in the cascade interaction between reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species and the NF-κB signaling pathway in liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 6): 1454- 1460. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.06.031.闵远骞, 李姗, 刘湘花, 等. 活性氧/活性氮与NF-κB信号通路级联交互在肝纤维化中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 6): 1454- 1460. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.06.031. [18] YANG L, WANG H, YANG X, et al. Auranofin mitigates systemic iron overload and induces ferroptosis via distinct mechanisms[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5( 1): 138. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-00253-0. [19] ZHANG CG. Essential functions of iron-requiring proteins in DNA replication, repair and cell cycle control[J]. Protein Cell, 2014, 5( 10): 750- 760. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-014-0083-7. [20] CHEUNG JCT, DENG GZ, WONG N, et al. More than a duologue: In-depth insights into epitranscriptomics and ferroptosis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 982606. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.982606. [21] PERSICHINI T, MAIO N, DI PATTI MCB, et al. Interleukin-1β induces ceruloplasmin and ferroportin-1 gene expression via MAP kinases and C/EBPβ, AP-1, and NF-κB activation[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2010, 484( 2): 133- 138. DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.034. [22] PHAM CG, BUBICI C, ZAZZERONI F, et al. Ferritin heavy chain upregulation by NF-kappaB inhibits TNFalpha-induced apoptosis by suppressing reactive oxygen species[J]. Cell, 2004, 119( 4): 529- 542. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.10.017. [23] CHENG K, HUANG YQ, WANG CF. 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibited ferroptosis in zebrafish liver cells(ZFL) by regulating Keap1-Nrf2-GPx4 and NF-κB-hepcidin axis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 21): 11334. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222111334. [24] BEN-NERIAH Y, KARIN M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-κB as the matchmaker[J]. Nat Immunol, 2011, 12( 8): 715- 723. DOI: 10.1038/ni.2060. [25] GAO JL, LUO T, WANG JK. Gene interfered-ferroptosis therapy for cancers[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12( 1): 5311. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25632-1. [26] ZHANG SW, LI D, HE J, et al. Mechanism of ferroptosis mediated by the bromodomain protein subfamily 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in chemotherapy resistance of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2024, 49( 7): 844- 852. DOI: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.003536.张硕稳, 李丹, 贺静, 等. BRD4/NF-κB信号通路介导的铁死亡参与三阴性乳腺癌化疗耐药的机制[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2024, 49( 7): 844- 852. DOI: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.003536. [27] KUNDU S, N S, T DAK. Discovery of pharmacological agents for triple-negative breast cancer(TNBC): Molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation studies on 5-lipoxygenase(5-LOX) and nuclear factor kappa B(NF-κB)[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2024, 42( 17): 9076- 9089. DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2250449. [28] WANG JG, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. Isoliquiritin modulates ferroptosis via NF-κB signaling inhibition and alleviates doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer[J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 2023, 45( 4): 443- 454. DOI: 10.1080/08923973.2023.2165943. [29] DAIMON T, BHATTACHARYA A, WANG KY, et al. MUC1-C is a target of salinomycin in inducing ferroptosis of cancer stem cells[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10( 1): 9. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-023-01772-9. [30] LAN YF, YANG T, YUE Q, et al. IRP1 mediated ferroptosis reverses temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via affecting LCN2/FPN1 signaling axis depended on NFKB2[J]. iScience, 2023, 26( 8): 107377. DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107377. [31] CHEN JS, CHEN PH, SONG YJ, et al. STING upregulation mediates ferroptosis and inflammatory response in lupus nephritis by upregulating TBK1 and activating NF-κB signal pathway[J]. J Biosci, 2024, 49: 9. [32] FANG WL, SONG X, LI HL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibits oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis to improve interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome by reducing NF-κB[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2024, 1871( 7): 119766. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119766. [33] DODSON M, CASTRO-PORTUGUEZ R, ZHANG DD. NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis[J]. Redox Biol, 2019, 23: 101107. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101107. [34] YANG HR, WU SN, GAO Q. Dexmedetomidine alleviates ferroptosis in rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting the Nrf2 pathway[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2025, 30( 7): 921- 928. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2025.07.006.杨焕然, 吴胜男, 高琴. 右美托咪定抑制Nrf2通路减轻大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤铁死亡[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2025, 30( 7): 921- 928. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2025.07.006. [35] SIVANDZADE F, PRASAD S, BHALERAO A, et al. NRF2 and NF-κB interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: Molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches[J]. Redox Biol, 2019, 21: 101059. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.11.017. [36] GAO JM, MA CJ, XIA DY, et al. Icariside II preconditioning evokes robust neuroprotection against ischaemic stroke, by targeting Nrf2 and the OXPHOS/NF-κB/ferroptosis pathway[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2023, 180( 3): 308- 329. DOI: 10.1111/bph.15961. [37] ZHU KY, ZHU X, LIU SQ, et al. Glycyrrhizin attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by inhibiting ferroptosis and neuroinflammation in neonatal rats via the HMGB1/GPX4 pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 8438528. DOI: 10.1155/2022/8438528. [38] GAO YL, ZHANG HJ, WANG JW, et al. Annexin A5 ameliorates traumatic brain injury-induced neuroinflammation and neuronal ferroptosis by modulating the NF-κB/HMGB1 and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 114: 109619. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109619. [39] GUO SL, LEI Q, GUO HN, et al. Edaravone attenuates aβ 1-42-induced inflammatory damage and ferroptosis in HT22 cells[J]. Neurochem Res, 2023, 48( 2): 570- 578. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-022-03782-y. [40] LI SB, HE YP, CHEN KX, et al. RSL3 drives ferroptosis through NF-κB pathway activation and GPX4 depletion in glioblastoma[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 2915019. DOI: 10.1155/2021/2915019. [41] ARAUZ J, RAMOS-TOVAR E, MURIEL P. Redox state and methods to evaluate oxidative stress in liver damage: From bench to bedside[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2016, 15( 2): 160- 173. DOI: 10.5604/16652681.1193701. [42] GIRARDIN SE, BONECA IG, VIALA J, et al. Nod2 is a general sensor of peptidoglycan through muramyl dipeptide(MDP) detection[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278( 11): 8869- 8872. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C200651200. [43] CHEN Q, ZHANG QQ, CAO P, et al. NOD2-mediated HDAC6/NF-κB signalling pathway regulates ferroptosis induced by extracellular histone H3 in acute liver failure[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2022, 26( 21): 5528- 5538. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17582. [44] ZHONG X, ZHANG ZG, SHEN H, et al. Hepatic NF-κB-inducing kinase and inhibitor of NF-κB kinase subunit α promote liver oxidative stress, ferroptosis, and liver injury[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2021, 5( 10): 1704- 1720. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1757. [45] LUEDDE T, BERAZA N, KOTSIKORIS V, et al. Deletion of NEMO/IKKgamma in liver parenchymal cells causes steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2007, 11( 2): 119- 132. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.12.016. [46] TAK J, JOO MS, KIM YS, et al. Dual regulation of NEMO by Nrf2 and miR-125a inhibits ferroptosis and protects liver from endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced injury[J]. Theranostics, 2024, 14( 5): 1841- 1859. DOI: 10.7150/thno.89703. [47] LIN YB, SHENG MW, QIN H, et al. Caspase 6 promotes innate immune activation by functional crosstalk between RIPK1-IκBα axis in liver inflammation[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21( 1): 282. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01287-x. [48] GUO XY, YIN XZ, LIU ZJ, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) pathogenesis and natural products for prevention and treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 24): 15489. DOI: 10.3390/ijms232415489. [49] ZHANG H, ZHANG EX, HU HB. Role of ferroptosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its implications for therapeutic strategies[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9( 11): 1660. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9111660. [50] YAO C, LAN DM, LI X, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis triggers inflammation in hepatocyte depend on ferroptosis via activating the NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Oral Dis, 2024, 30( 3): 1680- 1694. DOI: 10.1111/odi.14537. [51] YU LD, HE MY, LIU SH, et al. Fluorescent egg white-based carbon dots as a high-sensitivity iron Chelator for the therapy of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by iron overload in zebrafish[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13( 46): 54677- 54689. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c14674. [52] YUAN XW, LI L, ZHANG Y, et al. Heme oxygenase 1 alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing hepatic ferroptosis[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2023, 22( 1): 99. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-023-01855-7. [53] CHEN LJ, ZHOU HJ, CHENG ZY, et al. Role of ferroptosis in ALD: Focusing on hepcidin and besides hepcidin[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2024. DOI: 10.2174/0109298673317526240924050651. [54] WU XG, YUNG LM, CHENG WH, et al. Hepcidin regulation by BMP signaling in macrophages is lipopolysaccharide dependent[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7( 9): e44622. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044622. [55] ZMIJEWSKI E, LU SZ, HARRISON-FINDIK DD. TLR4 signaling and the inhibition of liver hepcidin expression by alcohol[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20( 34): 12161- 12170. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12161. [56] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. [57] YAO F, DENG YL, ZHAO Y, et al. A targetable LIFR-NF-κB-LCN2 axis controls liver tumorigenesis and vulnerability to ferroptosis[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12( 1): 7333. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27452-9. [58] SUN YW, HUANG D, LI JZ, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-NF-κB pathway facilitates SSPH I-induced ferroptosis in HepG2 cells[J]. Med Oncol, 2024, 41( 7): 184. DOI: 10.1007/s12032-024-02425-2. [59] WANG YF, FENG JY, ZHAO LN, et al. Aspirin triggers ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through restricting NF-κB p65-activated SLC7A11 transcription[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44( 8): 1712- 1724. DOI: 10.1038/s41401-023-01062-1. [60] LIN YJ, CHEN K, ZHU M, et al. Atractylenolide II regulates the proliferation, ferroptosis, and immune escape of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inactivating the TRAF6/NF-κB pathway[J]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 2024, 397( 10): 7697- 7710. DOI: 10.1007/s00210-024-03046-2. [61] LI ZL, KIM W, UTTURKAR S, et al. DDX5 deficiency drives non-canonical NF-κB activation and NRF2 expression, influencing sorafenib response and hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15( 8): 583. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06977-z. [62] MU M, HUANG CX, QU C, et al. Targeting ferroptosis-elicited inflammation suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and enhances sorafenib efficacy[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84( 6): 841- 854. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1796. -



 PDF下载 ( 984 KB)
PDF下载 ( 984 KB)

 下载:
下载:


