低病毒载量HBeAg阴性不确定期慢性HBV感染者肝组织病理分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250108
Liver histopathological features of HBeAg-negative patients in the indeterminate phase of low-viral-load chronic hepatitis B virus infection
-
摘要:
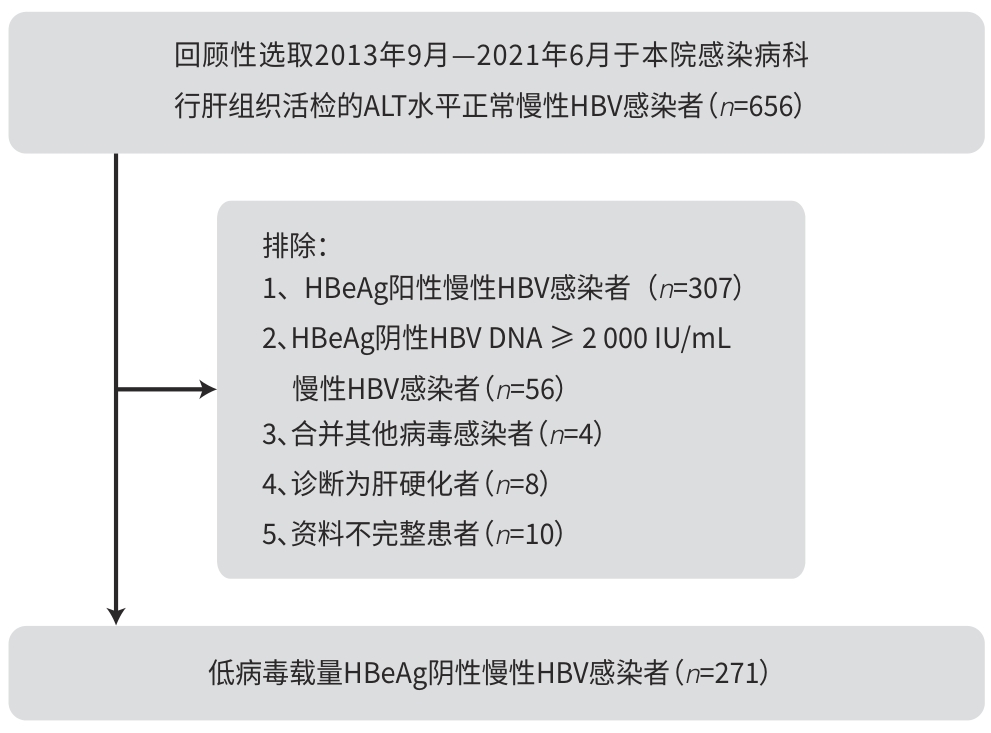
目的 分析低病毒载量HBeAg阴性不确定期慢性HBV感染者肝组织病理特征。 方法 选取2013年9月—2021年6月于延安大学附属医院感染病科行肝组织活检的271例低病毒载量HBeAg阴性慢性HBV感染者作为研究对象,比较不同年龄、性别、乙型肝炎家族史、HBsAg及ALT水平患者的肝组织损伤程度。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。 结果 271例HBeAg阴性慢性HBV感染者中86例(31.73%)肝组织炎症活动度≥A2、72例(26.57%)肝纤维化分期≥F2,112例(41.33%)患者存在中、重度肝组织损伤。ALT>20 U/L患者中肝组织炎症活动度≥A2比例高于ALT≤20 U/L患者,差异有统计学意义(χ2=3.938,P=0.047)。不同年龄、性别、乙型肝炎家族史、HBsAg水平患者的肝组织炎症活动度≥A2比例差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05);不同年龄、性别、乙型肝炎家族史、HBsAg水平、ALT水平患者的肝纤维化分期≥F2比例差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05);进一步对年龄≤30岁和无乙型肝炎家族史患者进行分层分析,结果显示肝组织炎症活动度≥A2比例和肝纤维化分期≥F2比例的组间差异亦无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。不同年龄、性别、乙型肝炎家族史、HBsAg水平、ALT水平等临床特征患者的肝组织损伤程度差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。 结论 超过40%的低病毒载量HBeAg阴性慢性HBV感染者肝组织存在显著损伤,不同年龄、性别、乙型肝炎家族史、HBsAg及ALT水平患者的肝组织损伤程度未见明显差异,即使年龄<30岁否认乙型肝炎家族史,患者仍有相当比例的肝组织存在损伤,需要引起临床医师的重视。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the liver histopathological features of HBeAg-negative patients in the indeterminate phase of low-viral-load chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Methods A total of 271 patients with low-viral-load HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection who underwent liver biopsy in Department of Infectious Diseases, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, from September 2013 to June 2021 were enrolled as subjects, and the degree of liver injury was compared between patients based on age, sex, presence or absence of the family history of hepatitis B, HBsAg, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level. The chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. Results Among the 271 patients with HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection, 86 patients (31.73%) grade≥A2 liver inflammatory activity, 72 (26.57%) had a liver fibrosis stage of ive, and 112 (41.33%) had moderate or severe liver histological injury. The proportion of patients with grade≥A2 liver inflammatory activity in the patients with ALT>20 U/L was significantly higher than that in the patients with ALT≤20 U/L (χ2=3.938, P=0.047). There were no significant differences in the proportion of patients with grade≥A2 liver inflammatory activity between the patients with different ages, sexes, family history of hepatitis B, HBsAg levels (all P>0.05),there were no significant differences in the proportion of patients with a liver fibrosis stage of ≥F2 between the patients with different ages, sexes, family history of hepatitis B, HBsAg, and ALT levels (all P>0.05), and the stratified analysis of patients aged≤30 years and patients without the family history of hepatitis B showed no statistical significance between groups (all P>0.05). There was no significant difference in the degree of liver histological injury between the patients with different ages, sexes, family history of hepatitis B, HBsAg, and ALT levels (all P>0.05). Conclusion Significant liver injury is observed in more than 40% of the patients with low-viral-load HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection, and there is no significant difference in the degree of liver histological injury between the patients with different ages, sexes, family history of hepatitis B, HBsAg, and ALT levels. Even for the patients aged≤30 years who deny the family history of hepatitis B, there is still a considerable proportion of patients with liver injury, which should be taken seriously by clinicians. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis B, Chronic /
- Viral Load /
- Inflammation /
- Hepatic Fibrosis /
- Liver Injury
-
表 1 低病毒载量HBeAg阴性不确定期慢性HBV感染者一般特征
Table 1. General characteristics of low viral load HBeAg negative chronic HBV infection with indeterminate phase
指标 数值 年龄(岁) 41(32~48) 男[例(%)] 120(44.28) 有乙型肝炎家族史[例(%)] 136(50.18) HBsAg(IU/mL) 2 477.62(591.20~5 807.00) 抗-HBe(S/CO) 0.01(0.01~0.02) 抗-HBc(S/CO) 9.73±1.48 HBV DNA(IU/mL) 510(241~988) ALT(U/L) 20(15~27) AST(U/L) 22(18~26) Alb(g/L) 43.1(40.0~46.3) LSM(kPa) 4.6(4.0~5.3) 肝脏炎症活动度分级[例(%)] <A2 185(68.27) ≥A2 86(31.73) 肝纤维化分期[例(%)] <F2 199(73.43) ≥F2 72(26.57) 中、重度肝组织损伤[例(%)] 无 159(58.67) 有 112(41.33) 表 2 不同临床特征的慢性 HBV 感染者肝组织炎症及肝纤维化的比较
Table 2. Comparison of liver inflammation and fibrosis of chronic HBV infected patients with different clinical characteristics
因素 炎症活动度 肝纤维化分期 <A2 ≥A2 χ2值 P值 <F2 ≥F2 χ2值 P值 年龄(例) 2.226 0.136 0.528 0.445 ≤30岁 40 12 36 16 >30岁 145 74 163 56 性别(例) 1.060 0.303 0.001 0.974 男 78 42 88 32 女 107 44 111 40 乙型肝炎家族史(例) 3.189 0.074 1.292 0.256 有 86 50 104 32 无 99 36 95 40 年龄≤30岁者乙型肝炎家族史(例) 0.599 0.439 0.109 0.742 有 15 6 14 7 无 25 6 22 9 无乙型肝炎家族史(例) 1.100 0.294 0.007 0.934 ≤30岁 25 6 22 9 >30岁 74 30 73 31 HBsAg(例) 0.532 0.466 0.309 0.579 <1 000 IU/mL 62 25 62 25 ≥1 000 IU/mL 123 61 137 47 ALT(例) 3.938 0.047 0.065 0.798 ≤20 U/L 102 37 103 36 >20 U/L 82 50 96 36 表 3 不同临床特征的慢性HBV感染者肝组织显著损伤的比较
Table 3. Comparison of significant liver tissue injury of chronic HBV infected patients with different clinical characteristics
因素 轻度肝组织损伤 中、重度肝组织损伤 χ2值 P值 年龄(例) 0.277 0.599 ≤30岁 32 20 >30岁 126 93 性别(例) 0.540 0.462 男 67 53 女 91 60 乙型肝炎家族史(例) 0.319 0.572 有 77 59 无 81 54 年龄≤30岁者乙型肝炎家族史(例) 0.288 0.592 有 12 9 无 20 11 无乙型肝炎家族史(例) 0.342 0.559 ≤30岁 20 11 >30岁 61 43 HBsAg(例) 0.114 0.736 <1 000 IU/mL 52 35 ≥1 000 IU/mL 106 78 ALT(例) 0.952 0.329 ≤20 U/L 85 54 >20 U/L 73 59 -
[1] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(2022 version)[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2023, 4( 1): 3- 28. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn11365-20230220-00050.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2023, 41( 1): 3- 28. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20230220-00050. [2] YAO K, LIU J, WANG J, et al. Distribution and clinical characteristics of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the grey zone[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2021, 28( 7): 1025- 1033. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13511. [3] ZHAN J, WANG J, ZHANG Z, et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of significant liver inflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis B in the indeterminate phase[J]. Virulence, 2023, 14( 1): 2268497. DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2268497. [4] HUANG DQ, LI X, LE MH, et al. Natural history and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in untreated chronic hepatitis B patients with indeterminate phase[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20( 8): 1803- 1812. e 5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.019. [5] HUANG DQ, TRAN A, YEH ML, et al. Antiviral therapy substantially reduces HCC risk in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection in the indeterminate phase[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 78( 5): 1558- 1568. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000459. [6] MARTIN P, NGUYEN MH, DIETERICH DT, et al. Treatment algorithm for managing chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the United States: 2021 update[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20( 8): 1766- 1775. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.036. [7] KAO JH, HU TH, JIA J, et al. East Asia expert opinion on treatment initiation for chronic hepatitis B[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 52( 10): 1540- 1550. DOI: 10.1111/apt.16097. [8] WEI S, XIE Q, LIAO G, et al. Patients with chronic hepatitis B who have persistently normal alanine aminotransferase or aged<30 years may exhibit significant histologic damage[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2024, 24( 1): 120. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03208-9. [9] RUGGIERI A, GAGLIARDI MC, ANTICOLI S. Sex-dependent outcome of hepatitis B and C viruses infections: synergy of sex hormones and immune responses?[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2302. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02302. [10] NING HB, JIN HM, LI K, et al. Liver pathological characteristics and the value of serum non-invasive diagnostic model in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal alanine aminotransferase and negative hepatitis B antigen[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2022, 40( 12): 729- 734. DOI: 103760/cma.j.cn311365-20220321-0009.宁会彬, 靳慧鸣, 李宽, 等. 丙氨酸转氨酶正常的乙型肝炎e抗原阴性慢性乙型肝炎患者的肝脏病理特征及血清学无创诊断模型价值分析[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2022, 40( 12): 729- 734. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20220321-0009. [11] SONNEVELD MJ, BROUWER WP, HANSEN BE, et al. Very low probability of significant liver inflammation in chronic hepatitis B patients with low ALT levels in the absence of liver fibrosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 52( 8): 1399- 1406. DOI: 10.1111/apt.16067. [12] GAO Y, WANG M, LIU X. Noninvasive serum markers for predicting significant liver histopathology in HBeAg-negative chronic HBV-infected patients with normal alanine aminotransferase[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2024, 12( 4): e0394123. DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.03941-23. [13] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Expert opinion on expanding anti-HBV treatment for chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2022, 30( 2): 131- 136. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220209-00060.中华医学会肝病学分会. 扩大慢性乙型肝炎抗病毒治疗的专家意见[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2022, 30( 2): 131- 136. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220209-00060. [14] DUAN M, CHI X, XIAO H, et al. High-normal alanine aminotransferase is an indicator for liver histopathology in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatol Int, 2021, 15( 2): 318- 327. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-021-10153-2. -



 PDF下载 ( 740 KB)
PDF下载 ( 740 KB)

 下载:
下载:


